Unit 7: Attitude & Social Cognition – covering all questions with Full Explanations
Q1. Which of the following best explains the concept of social influence in psychology?
Answer – B) The ways people impact and are impacted by others
Explanation: Social influence in psychology refers to how individuals’ thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are shaped by the presence and actions of others. It includes conformity, obedience, and persuasion, which are key areas in social psychology.
Q2. When someone begins using environmentally friendly items after noticing others do the same, this is an example of:
Answer – C) Social influence
Explanation: This behavior change occurs due to the influence of peers, which is a classic example of social influence. It shows how observing others can lead to adopting similar behaviors to fit in or be accepted.
Q3. The field of psychology that studies how people influence each other is known as:
Answer – C) Social psychology
Explanation: Social psychology is the branch that focuses on how people think about, influence, and relate to one another. It explores attitudes, group dynamics, persuasion, and behavior in social contexts.
Q4. The principle that behavior is influenced by the real or imagined presence of others is central to:
Answer – C) Social influence
Explanation: Social influence highlights how our actions are shaped not only by those physically present but even by their imagined presence. This principle explains conformity, peer pressure, and role expectations.
Q5. What does the concept of social facilitation suggest?
Answer – C) Task performance improves in the presence of others
Explanation: Social facilitation refers to improved performance on simple or well-learned tasks when others are watching. It happens because the presence of others increases arousal, which enhances dominant responses.
Q6. In psychology, which of the following best defines a group?
Answer – C) Two or more individuals who interact and influence each other
Explanation: In psychology, a group is defined by mutual interaction and influence. It’s not just about being physically together, but about individuals affecting each other’s behavior, thoughts, and feelings through direct or indirect contact.
Q7. What feature best describes a primary group?
Answer – C) Intimate, face-to-face interactions
Explanation: Primary groups are those with deep emotional connections and close, personal contact. Family, close friends, and childhood peer groups are examples. They are important for emotional development and identity.
Q8. When does a person’s sense of belongingness grow stronger?
Answer – C) Supportive social groups
Explanation: Being in a group that offers acceptance, understanding, and emotional support boosts a person’s sense of belonging, which is a basic psychological need. Belongingness contributes to self-worth and well-being.
Q9. Which of the following is an example of a primary group?
Answer – C) Family members
Explanation: Family is a primary group because it involves deep emotional bonds, frequent face-to-face contact, and long-term relationships. It’s where individuals first learn social norms and build their identity.
Q10. What is the function of a reference group?
Answer – B) A group that guides an individual’s behavior and attitudes
Explanation: A reference group is any group that a person refers to when forming attitudes, values, beliefs, or behavior—even if they are not a part of it. It influences decision-making and social comparison.
Q11. What does the term “social loafing” describe in group settings?
Answer – B) Declining effort when working in a group
Explanation: Social loafing occurs when individuals put in less effort while working in a group compared to when they work alone, often because they feel less accountable.
Q12. What does the concept of group polarization explain?
Answer – B) A group shifting to more extreme decisions
Explanation: Group polarization is when discussions within a group lead members to make more extreme decisions than they would on their own, often reinforcing shared opinions.
Q13. When a group discusses a commonly shared belief and ends up making a more extreme decision, it is known as:
Answer – D) Group polarization
Explanation: Group polarization happens when discussion among group members, who already share similar views, leads to stronger or riskier positions than before.
Q14. In which of the following conditions is social loafing more likely to occur?
Answer – C) Task has little value for individuals
Explanation: People tend to reduce effort when they don’t find personal meaning in the group task or believe their contribution won’t be recognized.
Q15. What is one potential danger of group polarization?
Answer – C) Rise in extreme attitudes or risky decisions
Explanation: Group polarization can push members toward more radical, risky, or one-sided views, which may lead to poor or even dangerous outcomes in group decisions.
Q16. Which of the following is most effective in reducing social loafing during group tasks?
Answer – C) Giving individual accountability
Explanation: Social loafing can be reduced when each member knows their individual performance will be noticed or evaluated, which promotes responsibility and effort.
Q17. What is a major drawback of group polarization?
Answer – C) Rise in extreme attitudes or risky decisions
Explanation: Group polarization leads members to adopt more extreme positions after discussion, which can result in impulsive or one-sided decisions.
Q18. The tendency to conform to a group to gain acceptance and avoid rejection is called:
Answer – A) Normative social influence
Explanation: Normative influence occurs when individuals conform to be liked or accepted by others, even if they personally disagree with the group.
Q19. Which of the following factors most strongly increases conformity?
Answer – D) Desire to be accepted
Explanation: People often conform because they want to fit in and be approved by the group, making the need for social acceptance a powerful motivator.
Q20. What is it called when individuals put in less effort in a group compared to working alone?
Answer – C) Social loafing
Explanation: Social loafing is a common group phenomenon where individuals reduce their personal effort because they feel less personally accountable or believe others will cover for them.
Q21. A group’s influence that causes a person to perform better when others are watching is known as:
Answer – C) Social facilitation
Explanation: Social facilitation is the tendency to perform better on simple or well-practiced tasks when in the presence of others due to increased arousal.
Q22. When is obedience most likely to occur, according to research in social psychology?
Answer – C) The authority is seen as legitimate
Explanation: Obedience increases significantly when the person giving instructions is perceived to have real authority, such as a professional or institutional figure.
Q23. The presence of others typically enhances performance on:
Answer – C) Easy or well-learned tasks
Explanation: According to the theory of social facilitation, people tend to do better on simple or familiar tasks in front of an audience due to increased alertness and motivation.
Q24. Groupthink happens when:
Answer – C) Desire for harmony overrides realistic judgment
Explanation: Groupthink occurs when the need to maintain group agreement leads to ignoring warnings, suppressing doubts, and making poor decisions.
Q25. Which classic experiment revealed how far people will go in obeying authority figures?
Answer – B) Milgram’s shock experiment
Explanation: Stanley Milgram’s experiment tested how individuals obey authority figures even when it involves harming others, revealing the surprising power of obedience.
Q26. A sense of identity and belongingness with one’s group is called:
Answer – B) Social identity
Explanation: Social identity refers to an individual’s sense of who they are based on their group memberships and the emotional attachment they feel towards the group.
Q27. The likelihood of bystander intervention decreases as the number of witnesses increases. This is known as:
Answer – C) Diffusion of responsibility
Explanation: Diffusion of responsibility occurs when individuals in a group feel less personal obligation to act because they assume someone else will take responsibility.
Q28. An individual’s shift in behavior due to perceived pressure from a group, even without direct request, is:
Answer – C) Conformity
Explanation: Conformity involves changing one’s behavior or belief to match those of the group, typically due to social pressure, even if unspoken.
Q29. When people in a group exert less effort than when working individually, it is known as:
Answer – C) Social loafing
Explanation: Social loafing refers to the tendency of individuals to put in less effort when working in a group compared to when they are working alone.
Q30. A cohesive group ignores alternatives and seeks consensus at all costs. This situation describes:
Answer – C) Groupthink
Explanation: Groupthink occurs when group members prioritize unity and harmony over critical analysis, leading to poor decisions and suppression of dissenting opinions.
Q31. Which of the following actions is least likely to involve social influence?
Answer – C) Practicing yoga alone to improve concentration
Explanation: Social influence involves other people affecting our thoughts or behavior. Practicing yoga alone for personal benefit is a self-driven act, not shaped by social pressure or presence of others.
Q32. Who conducted a famous study showing how people might give wrong answers just to fit in with a group?
Answer – B) Solomon Asch
Explanation: Solomon Asch’s line experiment showed that people often conform to group opinions, even when those opinions are clearly incorrect, highlighting the power of group pressure.
Q33. Which one of these behaviors does not reflect social influence?
Answer – C) Practicing mindfulness to feel calm
Explanation: Mindfulness is a personal activity done to manage one’s inner state. It doesn’t involve external social pressure, unlike the other options that reflect group or authority influence.
Q34. A student begins studying late at night because their friends say it’s the best time. This is an example of:
Answer – B) Peer influence
Explanation: When behavior changes due to what friends or others say or do, it reflects peer influence—one of the strongest forms of social impact, especially in adolescence and youth.
Q35. A group becomes meaningful when:
Answer – C) There’s interaction, common aims, and cooperation
Explanation: A group is meaningful when members interact regularly, work toward shared goals, and rely on one another. These features create unity and purpose.
Q36. Which feature does not belong to a genuine group?
Answer – C) No interaction among individuals
Explanation: Interaction is a key ingredient of a real group. Without communication or contact among members, it cannot function as a group.
Q37. What does the idea of “entitativity” in group psychology describe?
Answer – B) Seeing a group as one unified whole
Explanation: Entitativity is the sense that a group is a single entity rather than just a collection of individuals, based on similarity, interaction, and shared goals.
Q38. Which example best fits a secondary group relationship?
Answer – C) Collaborating with classmates on an assignment
Explanation: Secondary groups are based on specific goals and limited emotional closeness, like working with classmates. Primary groups like family and close friends involve deeper emotional bonds.
Q39. One important reason people seek group membership is to fulfill their need for:
Answer – C) Feeling connected and finding identity
Explanation: Groups help people satisfy emotional needs for belongingness and form part of their identity, making them feel valued and connected to a larger whole.
Q40. Why do most people naturally join groups, according to psychological research?
Answer – C) To meet emotional, survival, and identity needs
Explanation: Groups provide support, safety, emotional comfort, and a sense of belonging—all of which are essential for both survival and psychological well-being.
Q41. Which situation shows someone’s in-group?
Answer – C) Spending time with close friends
Explanation: An in-group is the group a person belongs to and feels strong emotional attachment with, like close friends or family.
Q42. What does the term out-group mean?
Answer – C) A group viewed as separate from one’s own
Explanation: An out-group consists of individuals or groups seen as “not belonging” to one’s own group, often viewed as different or “them” versus “us.”
Q43. What is the major difference between a formal and an informal group?
Answer – C) Clear roles and set rules
Explanation: Formal groups have structured roles, responsibilities, and official rules, while informal groups are based on personal relationships and flexibility.
Q44. When a person models their behavior after a celebrity group, it shows influence of:
Answer – C) Reference group influence
Explanation: A reference group serves as a standard for self-evaluation or behavior, even if the person is not directly part of that group, like celebrities influencing fans.
Q45. A group created to complete a specific assignment, like a project team, is known as a:
Answer – C) Task-oriented group
Explanation: Task-oriented groups are formed with the main goal of completing a specific duty or project, often with clear roles and objectives.
Useful for Psychology Exam – Attitude and Social Cognition
1. Important People (Name + Contribution)
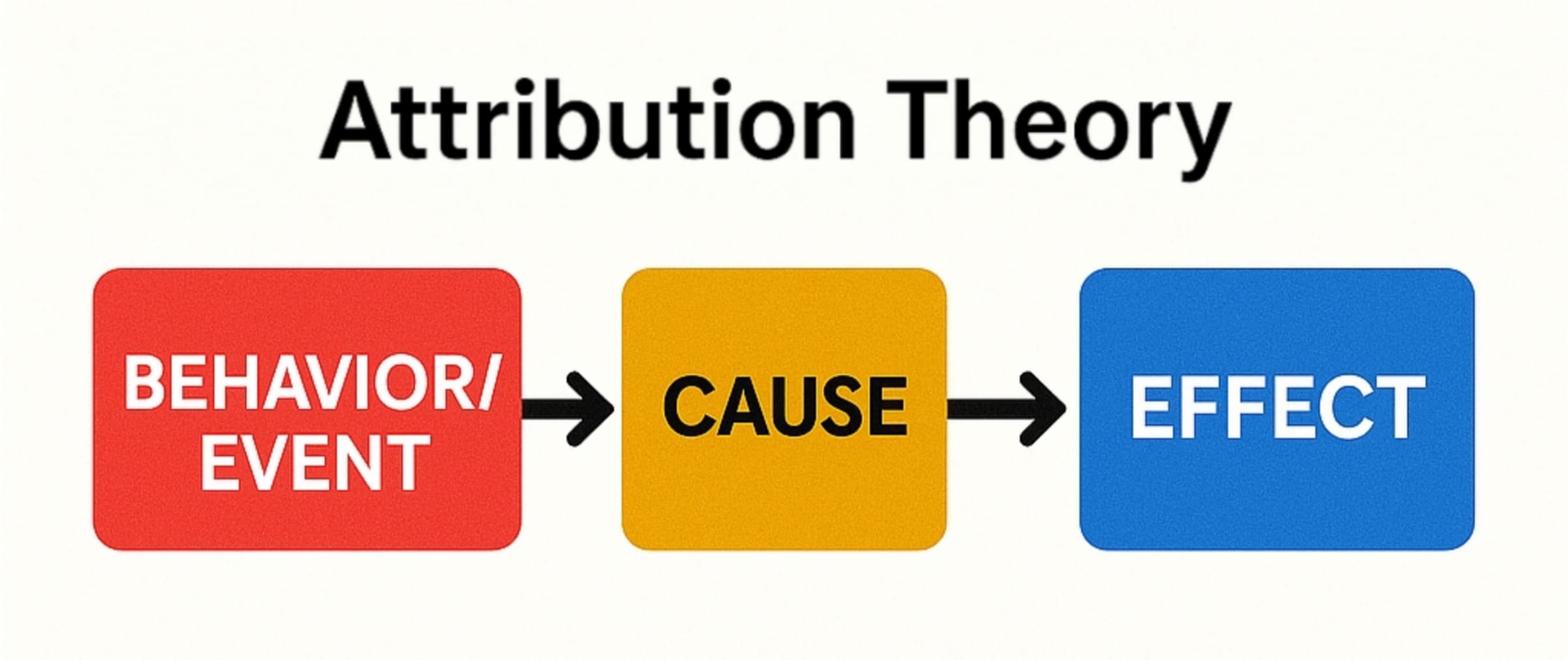
- Fritz Heider – Proposed Attribution Theory (explaining others’ behavior by internal or external causes)
- Leon Festinger – Developed Cognitive Dissonance Theory (conflict between attitudes and behaviors)
- Kelley – Introduced Covariation Model (how people assign cause to behavior)
- Bem – Self-Perception Theory (people infer attitudes from observing their own behavior)
2. Important Theories / Laws / Models
- Attribution Theory – Explaining causes of behavior (internal traits vs. external situations)
- Cognitive Dissonance Theory – Discomfort from holding conflicting thoughts, leading to attitude change
- Self-Perception Theory – Forming attitudes by observing one’s own behavior
- Attitude Formation – Shaped by direct experience, learning, and social factors
- Stereotypes, Prejudices, Discrimination – Preconceived beliefs, feelings, and behaviors towards groups
- Fundamental Attribution Error – Tendency to overemphasize personality traits and underplay situations
- Actor-Observer Bias – Attributing others’ behavior to character but our own to circumstances
- Self-Serving Bias – Taking credit for success but blaming failure on outside factors
3. Important Terms to Highlight
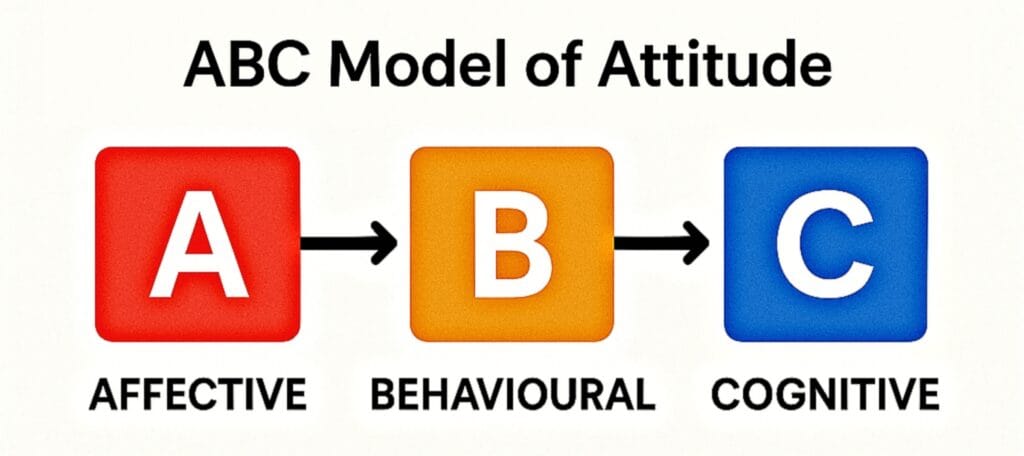
- Attitude – A learned tendency to evaluate things in a certain way
- Components of Attitude – Affective (feelings), Behavioral (actions), Cognitive (beliefs)
- Attribution – Process of explaining causes of behavior
- Fundamental Attribution Error – Overestimating internal causes
- Actor-Observer Bias – Different explanations for self vs others
- Self-Serving Bias – Favoring oneself in explanations
- Prejudice – Negative emotional attitude toward a group
- Stereotype – Oversimplified belief about a group
- Discrimination – Unfair behavior toward a group
- Cognitive Dissonance – Inner tension from conflicting attitudes and actions
- Impression Formation – Building an image of others
- Primacy Effect – First impressions are lasting
- Recency Effect – Recent information impacts impression
- Persuasion – Changing someone’s attitude
- Social Cognition – How we process, store, and apply information about others
4. Important Tables
Table: Components of Attitude
| Component | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affective | Feelings or emotions about something | Fear of snakes |
| Behavioral | Actions toward something | Avoiding snakes |
| Cognitive | Beliefs or thoughts about something | Snakes are dangerous |
Table: Attribution Types
| Attribution | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Internal (Dispositional) | Behavior due to personality | He is late because he is careless |
| External (Situational) | Behavior due to situation | He is late due to traffic jam |
Table: Common Biases
| Bias | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamental Attribution Error | Overemphasize personal factors | Blaming poor grades on laziness, not difficulty |
| Actor-Observer Bias | Different for self and others | I failed due to bad luck, others failed due to lack of effort |
| Self-Serving Bias | Taking credit for success | Winning because of skill, losing because of bad luck |

