Chapter 4: Biological Bases of Behavior PYQs & MCQs with full explanation
Q1. In a neuron, which structure mainly transmits signals away from the cell body to communicate with other neurons?
Answer – B) Axon
Explanation: The axon is the long, slender part of a neuron that carries electrical impulses away from the soma (cell body) toward other neurons, muscles, or glands. It plays a crucial role in sending information throughout the nervous system efficiently.
Q2. When a neuron is at rest, what type of electrical charge is predominantly found inside it?
Answer – D) Negative
Explanation: During the resting state, a neuron maintains a negative charge inside compared to the outside environment. This electrical difference, called the resting potential, is essential for the neuron to be ready to fire when needed.
Q3. How does the venom of a black widow spider impact the nervous system?
Answer – C) Agonist
Explanation: The venom acts as an agonist, meaning it mimics or enhances the action of neurotransmitters at the synapse, causing excessive stimulation of muscles and nerves, often leading to painful spasms and cramping.
Q4. Which technique involves applying a small electrical current to stimulate targeted areas of the brain without causing tissue damage?
Answer – C) Electrical Stimulation of the Brain (ESB)
Explanation: Electrical Stimulation of the Brain (ESB) uses mild electrical currents to activate specific parts of the brain, helping researchers understand brain functions. It is a safe, reversible method that does not cause permanent damage.
Q5. Dr. Roll needs to examine the brain’s white matter pathways. Which neuroimaging technique should she select?
Answer – B) Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
Explanation: Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) is a specialized form of MRI that maps the movement of water molecules along white matter tracts, allowing detailed visualization of connectivity pathways in the brain.
Q6. In the structure of a neuron, which component primarily receives incoming signals from neighboring cells?
Answer – B) Dendrite
Explanation: Dendrites are branch-like structures of a neuron that specialize in receiving information from other neurons. They act like antennas, picking up incoming messages and carrying them toward the cell body (soma).
Q7. Which endocrine gland plays the major role in controlling the body’s blood sugar levels?
Answer – C) Pancreas
Explanation: The pancreas releases insulin and glucagon, hormones that regulate blood sugar levels. Proper functioning of the pancreas ensures that glucose remains balanced in the bloodstream.
Q8. While oxytocin is popularly linked to trust and bonding, research suggests it can also enhance:
Answer – C) Attention to certain social stimuli
Explanation: Studies show that oxytocin sharpens our attention to social cues like facial expressions or emotional tone. It doesn’t just create trust; it also heightens awareness of social environments.
Q9. When you instinctively pull your hand away from a hot surface without conscious thought, it is an example of:
Answer – B) Reflex arc
Explanation: A reflex arc is an automatic, rapid response to a stimulus, handled by the spinal cord without needing brain involvement. It protects you from harm by reacting instantly.
Q10. Sensory neurons, responsible for carrying information toward the central nervous system, are classified as:
Answer – B) Only afferent neurons
Explanation: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) carry information from the body’s tissues and sensory organs toward the brain and spinal cord. They help the body detect stimuli like touch, pain, and temperature.
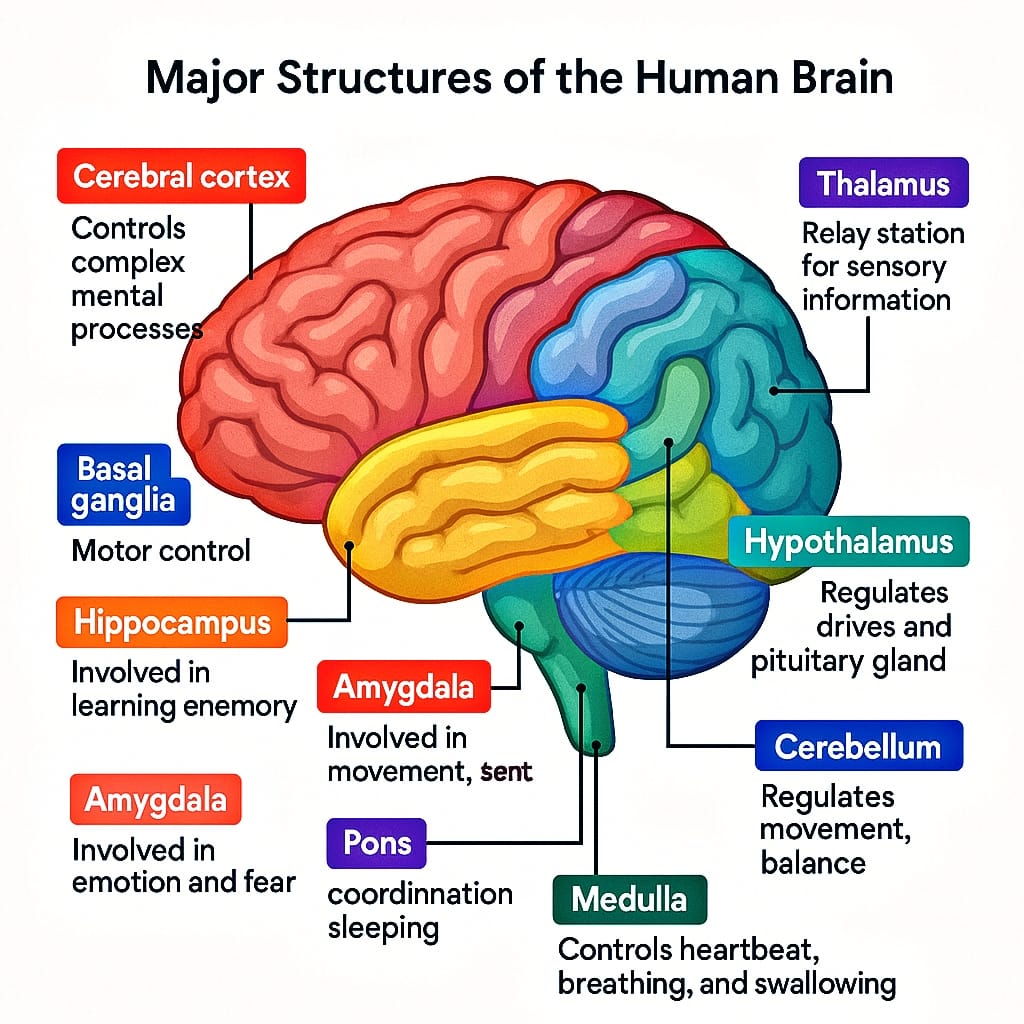
Q11. Which part of the nervous system would become highly active immediately after experiencing a car accident?
Answer – B) Sympathetic division
Explanation: The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system activates the “fight or flight” response, increasing heart rate, alertness, and energy to handle emergency situations like an accident.
Q12. If a person is unable to remember fear reactions to dangerous situations, damage is most likely in which brain structure?
Answer – C) Amygdala
Explanation: The amygdala processes emotions like fear and aggression. Damage to the amygdala can impair the ability to recognize or remember fear responses linked to threatening events.
Q13. In which lobe of the brain is the primary center for processing visual information located?
Answer – B) Occipital
Explanation: The occipital lobe at the back of the brain contains the primary visual cortex, which processes information related to sight.
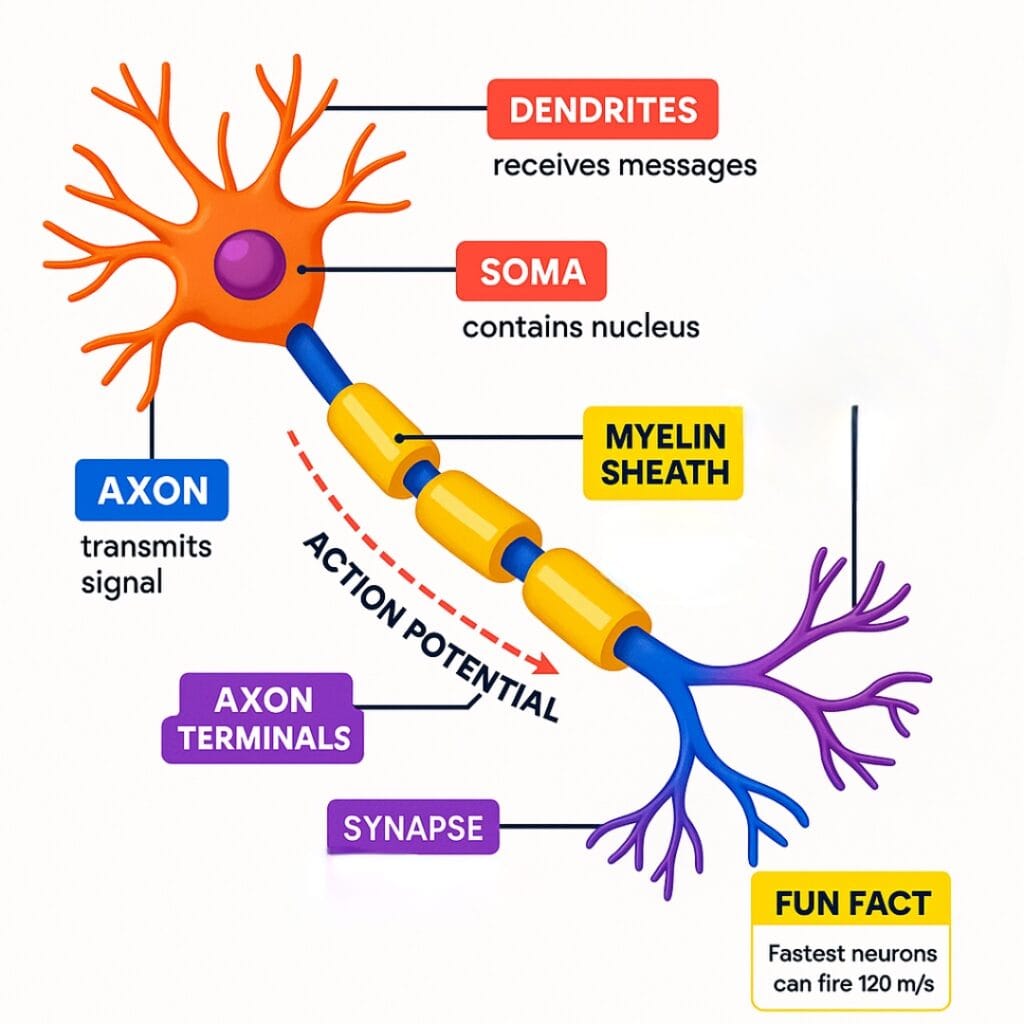
Q14. What structure wraps around the neuron’s axon to insulate it and speed up the transmission of electrical signals?
Answer – B) Myelin sheath
Explanation: The myelin sheath is a fatty covering around the axon that not only protects it but also significantly increases the speed of electrical signal transmission along the neuron.
Q15. Which neurotransmitter triggers skeletal muscle contractions while slowing down the heart rate?
Answer – B) Acetylcholine (ACh)
Explanation: Acetylcholine (ACh) stimulates skeletal muscles to contract but slows the heart’s activity by calming the cardiac muscles. It plays a key role in both the somatic and parasympathetic systems.
Q16. Bailey’s memory study involves applying magnetic pulses through copper coils placed near her scalp. Which technique is she using?
Answer – C) Noninvasive stimulation
Explanation: Noninvasive stimulation techniques, like Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), involve placing coils on the scalp to send magnetic pulses into the brain, affecting brain activity without surgery.
Q17. When Mary quickly awakens to outside noise after falling asleep, which part of her brain is likely responsible?
Answer – D) Reticular formation
Explanation: The reticular formation helps maintain alertness and filters incoming sensory signals. It plays a critical role in waking up to sudden sounds.
Q18. The “great relay station” of the brain, which directs sensory information to the proper areas, is known as the:
Answer – D) Thalamus
Explanation: The thalamus acts as the brain’s relay station by receiving incoming sensory information and directing it to the appropriate parts of the cortex for processing.
Q19. Johnson fell from her horse and injured the back of her head. Which sense is most likely to be affected due to damage to the occipital lobe?
Answer – B) Vision
Explanation: The occipital lobe is the primary center for visual processing, so damage to it can severely affect vision.
Q20. After brain injury, Emma speaks fluently but uses incorrect words in sentences. This may be a symptom of:
Answer – D) Wernicke’s aphasia
Explanation: Wernicke’s aphasia involves fluent speech but with nonsensical, incorrect, or unrelated words. Comprehension is often impaired too.
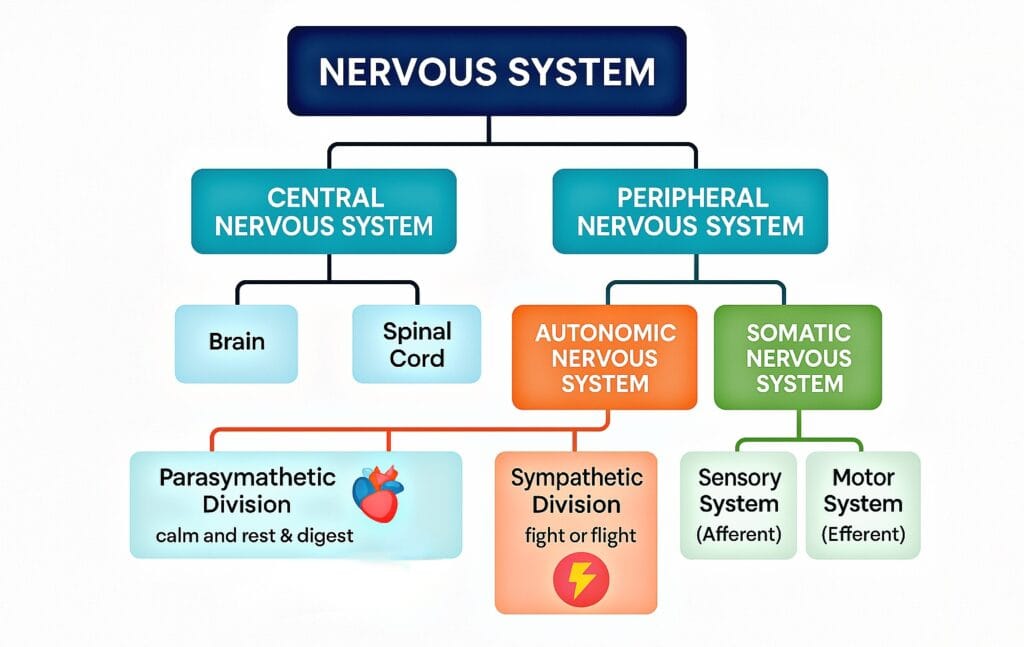
Q21. Involuntary muscles like those of internal organs are controlled by which nervous system division?
Answer – B) Autonomic
Explanation: The autonomic nervous system manages involuntary bodily functions like digestion, heartbeat, and gland activity without conscious control.
Q22. The somatosensory region of the cerebral cortex primarily processes which sense?
Answer – A) Touch
Explanation: The somatosensory cortex processes information related to touch, pressure, temperature, and body position.
Q23. Which hormone, produced by the pineal gland, rises during darkness and helps induce sleepiness?
Answer – A) Melatonin
Explanation: Melatonin is secreted by the pineal gland, increasing at night to promote sleep by regulating the body’s internal clock.
Q24. Neha’s fast heartbeat, rising blood pressure, and sweating before her speech were triggered by which part of the nervous system?
Answer – C) Sympathetic
Explanation: The sympathetic nervous system activates physiological changes during stress, such as increased heart rate, blood pressure, and sweating, preparing the body for action.
Q25. Growth in which brain region is most linked to the evolution of advanced human traits from primitive ancestors?
Answer – D) Neocortex
Explanation: The neocortex expanded significantly during human evolution, supporting complex thought, language, problem-solving, and planning abilities.
Q26. If a person damages their cerebellum in an accident, which ability would most likely be affected?
Answer – C) Coordinating movements
Explanation: The cerebellum is like the body’s “movement control center,” helping you balance, stay steady, and move smoothly. Damage here can make movements jerky or uncoordinated, almost like trying to walk while dizzy.
Q27. In the human brain, neurons make up approximately what percentage of all brain cells?
Answer – A) 20% neurons; 80% glial cells
Explanation: Although neurons get most of the attention, they are actually outnumbered by glial cells about 4 to 1. Glial cells act like the brain’s backstage crew — supporting, protecting, and feeding the neurons.
Q28. In the nervous system, which cells create the myelin coating around neurons in the brain and spinal cord, and which ones do so outside of it?
Answer – A) Oligodendrocytes; Schwann cells
Explanation: Think of oligodendrocytes as the brain and spinal cord’s “electricians,” while Schwann cells do the same job outside, in the body’s nerves. Both wrap neurons with myelin to speed up signal transmission.
Q29. In a neuron, what does the term “soma” refer to?
Answer – C) The cell body
Explanation: The “soma” is basically the neuron’s headquarters — the cell body that contains the nucleus and directs all cell activities. It’s the control center that keeps the neuron alive and functioning.
Q30. How many chromosomes are typically found in a normal human body cell?
Answer – B) 46
Explanation: Every normal human body cell has 46 chromosomes, arranged in 23 pairs. Half come from your mother and half from your father, carrying all your genetic information.
Q31. In the brain, the left hemisphere is mainly responsible for ________, while the right hemisphere focuses more on ________.
Answer – A) Verbal; Creative
Explanation: The left side of the brain is like your “language lab,” handling speaking, writing, and logical tasks. The right side is the “imagination station,” dealing with creativity, art, and visual skills.
Q32. Which of the following methods is NOT commonly used to study the brain?
Answer – D) TMS
Explanation: TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation) is used to stimulate brain areas, not primarily to study brain structure or function like MRI, PET, or CT scans do.
Q33. Which lobe of the brain plays the biggest role in controlling emotions and planning behavior?
Answer – A) Frontal lobe
Explanation: The frontal lobe is like your “CEO” — making decisions, controlling impulses, managing emotions, and helping you plan actions wisely.
Q34. In the limbic system, which structure acts like an alarm, detecting emotional threats?
Answer – B) Amygdala
Explanation: The amygdala works like your internal “danger detector,” quickly spotting emotional threats and preparing you to respond — whether it’s fear, anger, or excitement.
Q35. Which type of neurons carry sensory messages from the body to the brain?
Answer – C) Afferent neurons
Explanation: Afferent neurons are like “information couriers,” carrying messages from your senses (like touch or sight) up to your brain for processing.
Q36. What is the name of the electrical signal that travels along a neuron, causing it to send a message?
Answer – A) Action potential
Explanation: An action potential is like an electric “spike” that travels down the neuron, sending signals quickly and allowing communication across the nervous system.
Q37. Which major part of the brain houses the cerebrum and the limbic system?
Answer – A) Forebrain
Explanation: The forebrain is like the “command center” of the brain, managing thinking, emotions, memories, and voluntary actions through structures like the cerebrum and limbic system.
Q38. What is considered the fundamental building block of the entire nervous system?
Answer – A) Neuron
Explanation: Neurons are like the “tiny messengers” of the nervous system, carrying electrical and chemical signals to and from the brain and body.
Q39. Which division of the nervous system gets your body ready for quick action during emergencies?
Answer – B) Sympathetic nervous system
Explanation: The sympathetic nervous system acts like your “emergency team,” increasing heart rate, breathing, and energy to help you fight or flee during danger.
Q40. Which neurotransmitter is most strongly associated with mood balance and linked to depression?
Answer – B) Serotonin
Explanation: Serotonin acts like your “mood stabilizer.” When levels drop, it often leads to feelings of sadness and depression.
Q41. What is the small space between two neurons called, across which neurotransmitters are released to pass messages?
Answer – B) Synaptic gap
Explanation: The synaptic gap, also called the synaptic cleft, is the tiny space where neurotransmitters jump from one neuron to another to transmit signals.
Q42. Which brain structure acts like a “bridge” connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres?
Answer – C) Corpus callosum
Explanation: The corpus callosum is like a “communication highway” allowing the two hemispheres of the brain to share information quickly and smoothly.
Q43. If a person shows sudden shifts in personality and trouble managing emotions, which lobe is likely affected?
Answer – C) Frontal lobe
Explanation: The frontal lobe is crucial for personality, decision-making, emotional control, and planning behavior. Damage here often leads to dramatic changes.
Q44. Which gland is often called the “master gland” because it directs the activities of other glands?
Answer – B) Pituitary gland
Explanation: The pituitary gland controls the release of hormones from many other glands, guiding growth, metabolism, and reproductive processes.
Q45. Which part of the brain is mainly responsible for maintaining body balance and coordinating smooth movement?
Answer – C) Cerebellum
Explanation: The cerebellum acts like a “movement supervisor,” ensuring balance, posture, and coordinated, graceful actions.
Q46. Broca’s area in the brain plays a key role in which important ability?
Answer – B) Producing speech
Explanation: Broca’s area, located in the frontal lobe, is responsible for helping us physically produce clear and fluent speech. Damage here often leads to difficulty speaking words even though understanding remains intact.
Q47. Which hormone, secreted by the pineal gland, helps regulate the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle?
Answer – C) Melatonin
Explanation: Melatonin is the “sleep hormone” released by the pineal gland, especially in darkness, to help the body prepare for sleep.
Q48. How does an antagonist drug typically affect the way neurotransmitters work in the brain?
Answer – C) Blocking neurotransmitter action
Explanation: Antagonist drugs work by binding to neurotransmitter receptors and blocking them, preventing the natural chemical messages from being received by neurons.
Q49. What does the concept of neuroplasticity describe about the brain?
Answer – C) Brain’s ability to change connections
Explanation: Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s amazing ability to reorganize and form new neural connections, allowing learning, memory building, and recovery from injuries.
Q50. The right hemisphere of the brain is mainly specialized in managing which types of tasks?
Answer – C) Creativity and spatial tasks
Explanation: The right hemisphere is better at handling creativity, visual-spatial skills, art appreciation, and interpreting emotions, making it key for imaginative and nonverbal tasks.
Q51. Which of the following is NOT a function performed by glial cells in the nervous system?
Answer – D) Creating action potentials
Explanation: Glial cells support neurons by producing myelin, delivering nutrients, and cleaning up dead neurons, but they do not generate action potentials — that job belongs to neurons.
Q52. What is the term for the fluid-filled space that neurotransmitters cross to transmit a signal to another neuron?
Answer – C) Synapse
Explanation: The synapse is the tiny gap between two neurons where neurotransmitters are released to pass along a chemical message to the next cell.
Q53. Which neurotransmitter is primarily associated with reducing pain and creating feelings of pleasure?
Answer – B) Endorphins
Explanation: Endorphins are natural painkillers produced by the brain that help reduce discomfort and boost feelings of happiness and relaxation.
Q54. Which brain imaging technique tracks blood oxygen levels to observe real-time brain activity?
Answer – B) fMRI
Explanation: Functional MRI (fMRI) measures changes in blood oxygenation and flow that occur in response to neural activity, allowing scientists to see which parts of the brain are active.
Q55. If a doctor wants to record the electrical signals produced by brain neurons, which method would they choose?
Answer – D) Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Explanation: An EEG records the electrical patterns in the brain, providing valuable insights into brain states like sleep, alertness, and even epilepsy diagnosis.
Q56. Oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system both produce which important fatty substance?
Answer – C) Myelin
Explanation: Myelin is a fatty coating that wraps around axons, helping electrical impulses travel faster along nerve cells.
Q57. Ramesh manages to stay slim despite eating heavily. Which gland is most likely regulating his metabolism?
Answer – B) Thyroid
Explanation: The thyroid gland plays a key role in controlling metabolism. A faster metabolism helps in burning calories quickly, making it easier to stay thin.
Q58. Which gland is often referred to as the “master gland” because it directs other endocrine glands?
Answer – C) Pituitary
Explanation: The pituitary gland controls many other endocrine glands by releasing hormones that stimulate their activity, earning it the title of “master gland.”
Q59. What is the term for the brain’s ability to reorganize its structure and functions after injury or learning experiences?
Answer – B) Neuroplasticity
Explanation: Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to adapt, rewire itself, and form new neural connections, especially after damage or new learning.
Q60. Sophie ability to reach and pick up small objects relies mainly on which part of her nervous system?
Answer – B) Motor, somatic
Explanation: The somatic part of the nervous system controls voluntary muscle movements, and the motor pathway allows for actions like reaching and grabbing objects.
Q61. Which brain structure acts like a relay station, directing incoming sensory information to the correct regions of the brain for processing?
Answer – B) Thalamus
Explanation: The thalamus receives sensory information (except smell) and sends it to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex for further processing.
Q62. Which part of the brain is often referred to as the “rind” because it forms the outer covering?
Answer – A) Cortex
Explanation: The cortex is the brain’s outer layer, resembling a rind, where higher mental functions like reasoning, planning, and language occur.
Q63. A person dreams of forgetting how to move their limbs properly. This situation points to which disorder?
Answer – A) Apraxia
Explanation: Apraxia is a disorder where individuals have trouble planning and executing movements even though their muscles are fine.
Q64. In a neuron at rest, where is the negative charge found compared to the positive charge?
Answer – C) Inside, outside
Explanation: In a resting neuron, the inside is negatively charged relative to the outside due to differences in ion distribution.
Q65. Heroin mimics endorphins and blocks pain signals. What type of chemical action is heroin performing?
Answer – D) Agonist
Explanation: An agonist is a substance that mimics or enhances the action of a neurotransmitter. Heroin acts like endorphins, reducing pain.

