Unit 3: Meeting Life Challenges PYQs & MCQs with full explanations
Q1. In psychological terms, what does the concept of ‘stress’ primarily refer to?
Answer – B) A response to demanding situations
Explanation: Stress is a psychological and physiological reaction to situations that challenge or threaten an individual’s well-being or exceed their coping resources.
Q2. Which of the following best represents a source of environmental stress?
Answer – B) Loud noise in a neighborhood
Explanation: Environmental stressors are external factors such as noise, crowding, pollution, or natural disasters that disrupt comfort or functioning.
Q3. Which of the following statements about stress is factually correct?
Answer – C) It can sometimes improve performance
Explanation: Moderate levels of stress (eustress) can enhance alertness, motivation, and performance in tasks that require focus and energy.
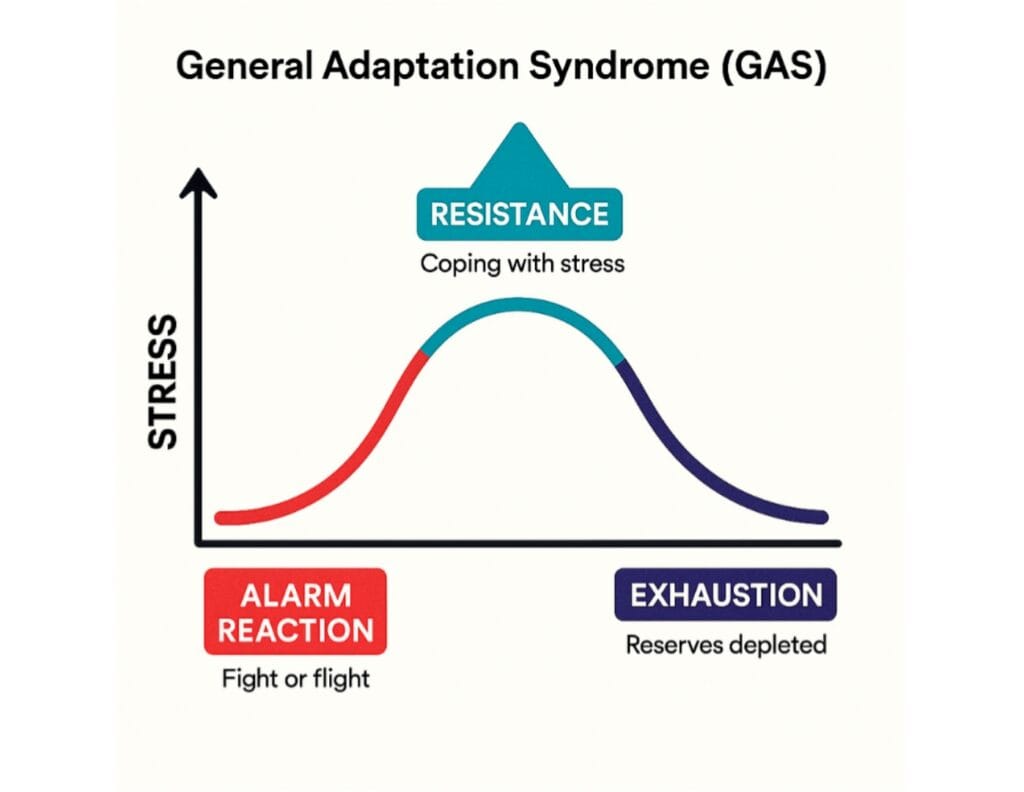
Q4. What happens to the body during the alarm stage of the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)?
Answer – C) Becomes alert and activated
Explanation: In the alarm stage, the body experiences a fight-or-flight reaction, marked by heightened physiological arousal to deal with a perceived threat.
Q5. Who formulated the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) model of stress response?
Answer – B) Hans Selye
Explanation: Hans Selye introduced the GAS model, explaining the body’s physiological response to chronic stress in three stages: alarm, resistance, and exhaustion.
Q6. During the alarm stage of stress response, the body:
Answer – B) Prepares for immediate action
Explanation: The alarm stage is the first phase in the stress response, where the body activates its fight-or-flight system to handle the perceived threat.
Q7. The resistance stage in the stress response is characterized by:
Answer – B) The body adapting to stress
Explanation: In the resistance stage, the body tries to cope with the stressor and return to a state of balance, while remaining on high alert internally.
Q8. The term cognitive appraisal refers to:
Answer – B) How individuals interpret and evaluate a stressor
Explanation: Cognitive appraisal, according to Lazarus, is how a person mentally evaluates whether a situation is stressful and how they can cope with it.
Q9. According to Lazarus, stress occurs when:
Answer – C) The demands exceed one’s perceived resources
Explanation: Lazarus emphasized that stress is psychological and arises when we see challenges as more than what we can handle.
Q10. Which of the following is an example of a chronic stressor?
Answer – C) Long-term illness
Explanation: Chronic stressors last for extended periods and include conditions like ongoing illness, which can drain coping resources over time.
Q11. What does the term “eustress” refer to in psychology?
Answer – C) A beneficial form of stress that enhances performance
Explanation: Eustress is a positive form of stress that can motivate individuals to achieve goals and face challenges productively.
Q12. Which of the following is considered a major life event stressor?
Answer – C) Loss of a loved one
Explanation: Life event stressors are significant changes that impact a person’s emotional well-being, such as the death of a close relative.
Q13. What area does psychoneuroimmunology explore?
Answer – C) Interactions between the mind, brain, and immune system
Explanation: Psychoneuroimmunology studies how stress influences health by affecting the relationships among psychological processes, the nervous system, and immunity.
Q14. Which of these is not a recommended way to cope with stress-related health problems?
Answer – B) Smoking to feel relaxed
Explanation: Smoking may provide temporary relief but worsens physical health and increases stress over time. Healthy methods like sleep, exercise, and relaxation techniques are more effective.
Q15. What does the General Adaptation Syndrome model describe?
Answer – B) Phases of the body’s response to stress
Explanation: The General Adaptation Syndrome, introduced by Hans Selye, outlines how the body reacts to prolonged stress in three stages: alarm, resistance, and exhaustion.
Q16. What typically happens to the body during the exhaustion stage of stress response?
Answer – C) It starts to weaken and becomes more prone to illness
Explanation: In the exhaustion phase, prolonged stress depletes the body’s energy, weakening the immune system and increasing vulnerability to illness.
Q17. What does the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) model explain?
Answer – B) The effects of long-term stress on the body
Explanation: The GAS model, proposed by Hans Selye, describes how the body responds to persistent stress in three phases: alarm, resistance, and exhaustion.
Q18. What does primary appraisal help us understand in stressful situations?
Answer – B) Assessing whether the event is harmful, challenging, or irrelevant
Explanation: Primary appraisal is the initial evaluation of a situation to determine if it poses a threat or challenge.
Q19. Which of the following is an example of problem-focused coping?
Answer – C) Actively planning steps to solve the issue
Explanation: Problem-focused coping involves taking direct steps to eliminate or reduce the stressor by finding practical solutions.
Q20. What is evaluated during the secondary appraisal process?
Answer – B) Assessing your available coping strategies and support
Explanation: In secondary appraisal, a person considers their ability to manage the stressor using resources, support, and coping skills.
Q21. What does emotion-focused coping mainly involve?
Answer – C) Managing emotional responses to the stressor
Explanation: Emotion-focused coping helps a person handle the emotional impact of stress, especially when the situation can’t be easily changed.
Q22. What is the main benefit of using effective coping strategies?
Answer – C) Supporting mental and physical well-being
Explanation: Healthy coping helps in reducing stress-related harm, promoting overall health and better functioning.
Q23. A student who regularly meditates and maintains a routine is most likely to:
Answer – C) Handle stress well and stay healthy
Explanation: Practices like meditation and time management are proven to reduce stress and support overall well-being.
Q24. Which method is widely recommended for managing stress?
Answer – B) Exercising regularly
Explanation: Regular physical activity helps the body release tension and improves mood, making it an effective stress-relief technique.
Q25. What is one of the main benefits of practicing meditation?
Answer – C) Developing inner calm and reducing stress
Explanation: Meditation trains the mind to relax and focus, helping in lowering stress levels and promoting emotional well-being.
Q26. How do deep breathing practices help in managing stress?
Answer – C) By triggering the body’s natural calming system
Explanation: Deep breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system, which slows down stress responses and helps the body relax.
Q27. When students actively seek resources to solve academic problems, what coping method are they using?
Answer – C) Problem-solving through direct action
Explanation: This is a clear example of problem-focused coping, where the person tries to handle the issue directly through planning or seeking help.
Q28. What is the primary purpose of Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)?
Answer – C) To relieve physical tension and reduce stress
Explanation: PMR is a relaxation method where muscle groups are tensed and then relaxed to release stored tension and promote calmness.
Q29. In stress relief practices, yoga is known for combining:
Answer – B) Mindfulness through movement, breath, and meditation
Explanation: Yoga combines physical postures, deep breathing, and meditative focus, helping reduce mental and physical stress effectively.
Q30. What best describes the concept of guided imagery in stress reduction?
Answer – B) Mentally visualizing serene and comforting images
Explanation: Guided imagery involves imagining peaceful and positive scenes to calm the body and mind, reducing anxiety and tension.
Q31. Which hormone is most closely linked with the body’s reaction to stress?
Answer – C) Cortisol
Explanation: Cortisol is the main stress hormone released by the adrenal glands, helping the body respond to challenging situations.
Q32. In Hans Selye’s General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS), what is the final stage when the body’s resources are depleted?
Answer – C) Exhaustion
Explanation: The exhaustion stage follows prolonged stress, where the body’s energy is drained, making it more vulnerable to illness.
Q33. A student who feels anxious before a test but uses that nervous energy to study harder is showing:
Answer – A) Positive stress (eustress)
Explanation: Eustress is a beneficial form of stress that motivates people to perform better under pressure.
Q34. Which behavior shows a problem-focused approach to managing stress?
Answer – C) Making a detailed plan to handle the situation
Explanation: Problem-focused coping involves addressing the source of stress directly through planning or action.
Q35. What best describes resilience in a stressful situation?
Answer – C) Adapting and recovering quickly from challenges
Explanation: Resilience is the ability to bounce back from stress or adversity, learning and growing from the experience.
Q36. Which of the following stress-reducing strategies benefits both the body and the mind?
Answer – C) Engaging in regular physical activity
Explanation: Regular exercise reduces stress hormones, improves mood, and strengthens the immune system.
Q37. What best defines a stressor?
Answer – B) Any demand — physical, mental, or social — that leads to stress
Explanation: A stressor is anything that challenges a person’s ability to cope, whether it’s external (like noise) or internal (like worry).
Q38. Which branch of psychology focuses on how stress affects health and wellbeing?
Answer – C) Health Psychology
Explanation: Health psychology examines how psychological factors like stress influence physical health, illness, and health behaviors.
Q39. Which of the following can contribute to increased psychological stress?
Answer – C) Disorganized time management
Explanation: Poor time management can cause deadline pressure, reduce productivity, and create ongoing stress.
Q40. Which coping method is commonly used when the situation cannot be changed?
Answer – C) Emotion-focused coping
Explanation: Emotion-focused coping helps manage feelings when the stressor is beyond one’s control, such as loss or irreversible situations.
Q41. Individuals with strong cognitive appraisal abilities are more likely to:
Answer – C) Handle stress with calmness and adaptability
Explanation: Cognitive appraisal allows individuals to assess a situation thoughtfully, leading to calm and flexible responses under pressure.
Q42. Which coping style focuses on handling emotional discomfort rather than directly fixing the problem?
Answer – C) Emotion-focused coping
Explanation: Emotion-focused coping deals with managing one’s emotional reaction, especially when the stressor cannot be directly changed.
Q43. A person who seeks comfort from a friend during a tough time is using which strategy?
Answer – B) Emotion-focused coping
Explanation: Talking to a friend for emotional relief is a typical emotion-focused approach to reduce distress.
Q44. Which of the following does not represent a problem-focused coping strategy?
Answer – D) Mentally suppressing the problem
Explanation: Suppressing or trying to forget the issue avoids addressing it directly, unlike problem-focused methods which involve action and solution.
Q45. What is a likely outcome of using poor coping strategies over time?
Answer – C) Greater risk of anxiety and health issues
Explanation: Ineffective coping may result in chronic stress, weakening mental and physical health over time.
Q46. Prolonged use of unhealthy coping methods is most likely to result in:
Answer – C) Increased health problems and ongoing stress
Explanation: Negative coping strategies like substance abuse or avoidance may provide short-term relief but often worsen physical and mental health over time.
Q47. According to studies, individuals with better coping abilities are more likely to:
Answer – B) Bounce back from stress and manage it well
Explanation: Adaptive coping enhances emotional and physical resilience, helping individuals manage stress and recover faster.
Q48. Extended exposure to stressful conditions may lead to:
Answer – C) Anxiety or depressive symptoms
Explanation: Chronic stress can disrupt brain chemistry and increase the risk of mental health disorders like depression and anxiety.
Q49. What type of stress is experienced during significant life changes, like moving to a new city?
Answer – C) Life event
Explanation: Major transitions such as relocation or a job change are classified as life events, which can trigger temporary stress responses.
Q50. Which situation best represents an acute form of stress?
Answer – B) Awaiting exam results
Explanation: Acute stress arises from short-term, high-pressure situations like waiting for important news or facing a deadline.
Q51. Which situation best illustrates a daily hassle as a source of stress?
Answer – C) Being stuck in traffic on a school day
Explanation: Daily hassles are minor, frequent disruptions or irritants that can add up to cause stress, like traffic jams or long queues.
Q52. In psychological terms, how is stress most accurately described?
Answer – B) A condition where one must adjust or respond to pressure
Explanation: Stress refers to the psychological and physical strain that arises when an individual faces challenges or demands requiring adjustment.
Q53. What does the term “homeostasis” mean in the context of stress and health?
Answer – B) A balanced internal state maintained by the body
Explanation: Homeostasis is the body’s process of keeping internal systems stable and in balance, which is disrupted under prolonged stress.
Q54. What is meant by a “life challenge” in psychological terms?
Answer – C) Situations that demand more than what a person can easily manage
Explanation: A life challenge refers to any situation that pushes a person’s coping resources to the limit, such as personal loss, transitions, or intense pressure.
Q55. What plays the biggest role in how a person reacts to a difficult situation?
Answer – C) Their interpretation of the situation
Explanation: A person’s cognitive appraisal, or how they evaluate a situation, strongly influences how stressful it feels and how they cope with it.
Useful for CUET UG Psychology: Meeting Life Challenges
1. Important People (Name + Contribution)
- Hans Selye – Proposed the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) model of stress (Alarm, Resistance, Exhaustion)
- Richard Lazarus – Gave the Cognitive Appraisal Theory of stress (Primary and Secondary appraisal)
- Albert Bandura – Introduced the concept of Self-efficacy as a personal coping resource
- Susan Kobasa – Introduced the idea of Hardiness (commitment, control, challenge) as a stress buffer
- Shelley Taylor – Proposed the concept of Tend and Befriend response to stress (especially among females)
2. Important Theories / Laws / Models
- General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) Model – Stress response in three stages: Alarm, Resistance, Exhaustion (Hans Selye)
- Cognitive Appraisal Model – Stress depends on individual’s interpretation (Primary: “Is it harmful?” and Secondary: “Can I cope?”) (Richard Lazarus)
- Hardiness Theory – A personality trait that buffers against stress (Susan Kobasa)
- Positive Health Model – Emphasizes resilience, optimism, and positive emotions in coping
- Life Skills Approach – Training skills like communication, problem-solving, time management to handle stress effectively
3. Important Terms to Highlight
- Stress – Physical and psychological reaction to demands exceeding resources
- Eustress – Positive, beneficial stress that motivates
- Distress – Negative, harmful stress
- General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) – Three-stage stress response: Alarm → Resistance → Exhaustion
- Cognitive Appraisal – Personal evaluation of an event’s significance for one’s well-being
- Primary Appraisal – Assessing whether an event is irrelevant, positive, or stressful
- Secondary Appraisal – Assessing available coping resources and options
- Coping – Efforts to manage internal and external demands of stressful situations
- Problem-focused coping – Dealing directly with the stressor (e.g., making a plan)
- Emotion-focused coping – Managing emotions related to the stressor (e.g., relaxation)
- Resilience – Ability to bounce back from adversity
- Hardiness – Personality trait characterized by commitment, control, and challenge
- Self-efficacy – Belief in one’s capacity to handle situations effectively
- Social Support – Emotional, informational, or practical help received from others
- Positive Health – A state of flourishing and well-being beyond just absence of illness
4. Important Tables
Table: Stages of General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
| Stage | Description | Body’s Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Alarm Reaction | Initial shock and mobilization of defenses | Fight or Flight response activated |
| Resistance | Body attempts to resist or cope with the stressor | Sustained physiological arousal |
| Exhaustion | Resources depleted; breakdown occurs | Increased risk of illness |
Table: Types of Coping Strategies
| Type | Example | Aim |
|---|---|---|
| Problem-focused coping | Making a plan, seeking help | Solve the problem |
| Emotion-focused coping | Meditation, venting emotions | Manage feelings |
Table: Differences between Eustress and Distress
| Basis | Eustress | Distress |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Positive stress | Negative stress |
| Effect | Motivates and enhances performance | Causes anxiety and reduces performance |
| Example | Preparing for a competition | Dealing with a job loss |

