Unit 2: Self and Personality PYQs & MCQs with full explanations
Q1. What does the study of “Self and Personality” in psychology primarily help us understand?
Answer – C) Internal processes and individual differences
Explanation: The study of self and personality focuses on understanding how people perceive themselves, how they behave, and what makes individuals unique in terms of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
Q2. In psychology, what does the term “self” refer to?
Answer – B) The way one views oneself
Explanation: In psychological terms, “self” refers to one’s self-concept — how individuals perceive and evaluate themselves, including their thoughts, beliefs, and identity.
Q3. Which of the following is a standardized self-report personality test?
Answer – B) MMPI
Explanation: The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) is a widely used self-report test that assesses various personality traits and psychological disorders using standardized questions.
Q4. What key concept did Carl Rogers emphasize in his theory of personality?
Answer – C) Unconditional positive regard
Explanation: Carl Rogers believed that for a person to grow and fulfill their potential, they need an environment that provides genuineness, acceptance, and unconditional positive regard.
Q5. According to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, what is the highest level a person can achieve?
Answer – D) Self-actualization
Explanation: Self-actualization is at the top of Maslow’s pyramid. It refers to realizing one’s full potential, creativity, and purpose after all basic and psychological needs are met.
Q6. Cultural approach helps understand:
Answer – B) Personality in diverse societies
Explanation: The cultural approach studies how personality is shaped by the values, beliefs, customs, and practices of different societies, highlighting how definitions of self vary across cultures.
Q7. Bandura’s social learning theory emphasizes:
Answer – A) Observational learning and modeling
Explanation: Albert Bandura’s theory focuses on how people learn behaviors through observing others and imitating them, especially when those behaviors are rewarded — a process called modeling.
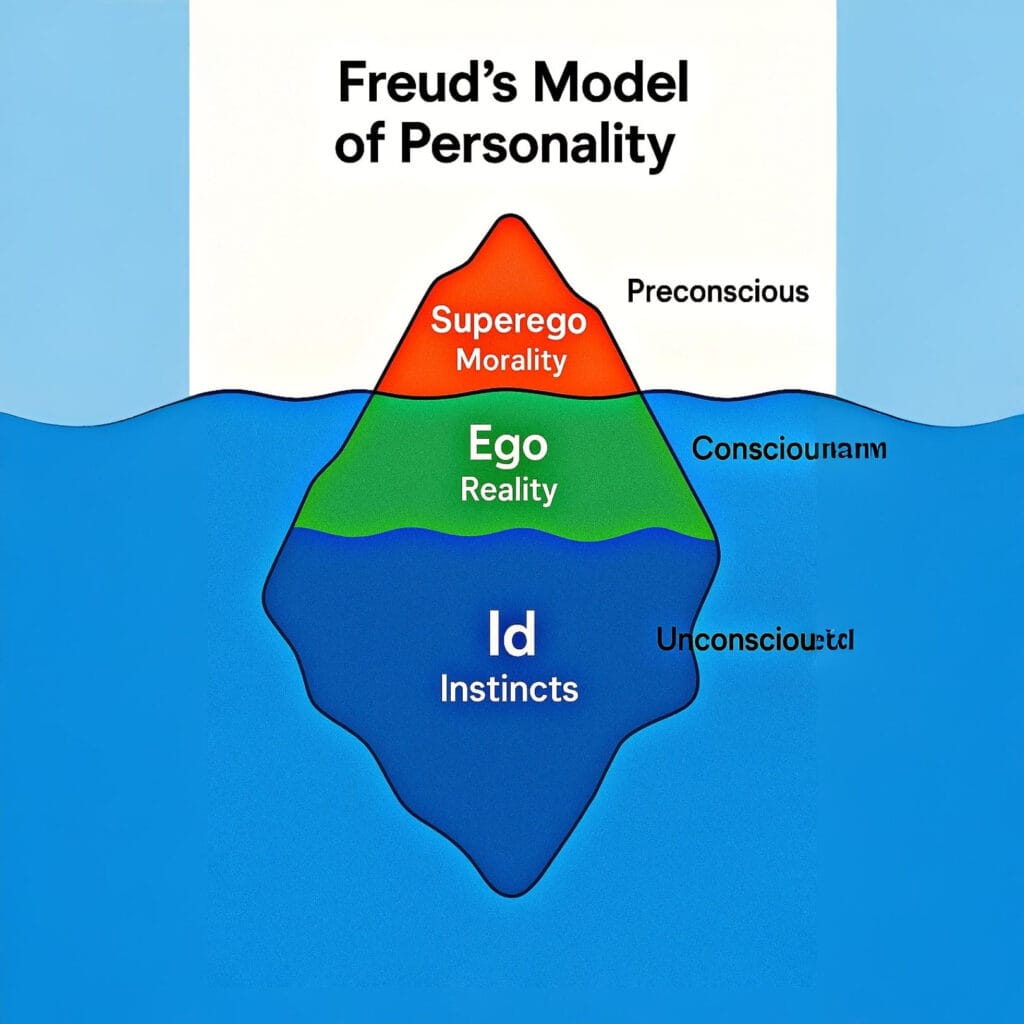
Q8. According to Freud, the id functions based on the:
Answer – B) Pleasure principle
Explanation: In Freud’s psychoanalytic theory, the id is the primitive part of the personality that seeks immediate gratification of desires and operates on the pleasure principle, without considering reality or morality.
Q9. A student resisting distractions to complete homework is showing:
Answer – B) Strong self-regulation
Explanation: Self-regulation involves the ability to control one’s behavior, emotions, and thoughts in pursuit of long-term goals. Resisting distractions reflects effective self-regulatory control.
Q10. High self-esteem in adolescents is usually associated with:
Answer – B) Positive self-concept and confidence
Explanation: Adolescents with high self-esteem usually have a positive view of themselves and are more confident in handling social, academic, and personal challenges.
Q11. In psychological assessment, an interview refers to which of the following?
Answer – B) Structured or unstructured verbal questioning
Explanation: Interviews in psychology involve either planned (structured) or open-ended (unstructured) conversations to gather in-depth personal information, making them a flexible and widely used method of assessment.
Q12. Which method is most effective for diagnosing emotional and mental issues in clinical settings?
Answer – C) Projective tests and case studies
Explanation: Projective techniques such as the TAT and Rorschach, along with detailed case studies, help reveal underlying thoughts, emotions, and personality dynamics critical for clinical diagnosis.
Q13. The Draw-A-Person Test is categorized under which type of psychological tool?
Answer – C) Projective technique
Explanation: The Draw-A-Person Test is a projective technique that uses drawings to uncover inner thoughts, emotions, and personality features, especially in children and non-verbal individuals.
Q14. What primarily shapes a person’s personality?
Answer – C) Both heredity and environment
Explanation: Personality is a result of the complex interaction between genetic makeup and life experiences, including family, culture, and education.
Q15. A student who remains positive and hopeful in different situations shows what kind of characteristic?
Answer – C) Positive personality trait
Explanation: Consistent optimism and cheerfulness reflect a **positive personality trait**, not just a momentary mood or condition. These are stable features over time.
Q16. How are personality traits generally understood in psychology?
Answer – C) Long-term and stable behavioral tendencies
Explanation: Personality traits refer to consistent patterns in behavior, thought, and emotion that remain stable across time and situations.
Q17. Which of the following correctly matches a cultural orientation with its typical value?
Answer – C) Collectivist – cooperation and harmony
Explanation: Collectivist cultures emphasize working together, maintaining relationships, and prioritizing the group over individual gain.
Q18. Which statement reflects an interdependent view of the self?
Answer – B) “I am part of my community, and we succeed together.”
Explanation: An interdependent self-concept emphasizes social roles, connectedness, and shared success within a group or community.
Q19. Someone who says, “I am unique, and I make my own choices,” is likely influenced by which cultural background?
Answer – C) Individualistic culture
Explanation: Individualistic cultures promote personal freedom, self-expression, and the belief that individuals are independent from groups.
Q20. In cultures that emphasize collectivism, personal identity is shaped mainly by:
Answer – C) Group goals and harmony
Explanation: Collectivist societies prioritize maintaining group unity, fulfilling social roles, and achieving common goals over personal ambitions.
Q21. Which of the following combinations reflects healthy psychological adjustment?
Answer – C) High esteem, high efficacy, strong self-regulation
Explanation: A psychologically well-adjusted person typically feels confident, believes in their ability to succeed, and can manage impulses and emotions effectively.
Q22. What is a common outcome of low self-esteem?
Answer – C) Lack of confidence and anxiety
Explanation: People with low self-esteem often struggle with self-doubt, leading to anxious feelings and reluctance to take on challenges.
Q23. Which of the following best shows high self-efficacy?
Answer – C) “I know I can handle this challenge.”
Explanation: High self-efficacy reflects belief in one’s ability to succeed in specific tasks or situations, which helps with goal setting and persistence.
Q24. A person who manages their time well and avoids impulsive behavior shows:
Answer – A) High self-regulation
Explanation: Self-regulation involves managing thoughts, behaviors, and emotions to achieve long-term goals, including time and emotional control.
Q25. What did Bandura describe as self-efficacy?
Answer – B) Confidence in your ability to perform specific tasks
Explanation: According to Albert Bandura, self-efficacy is the belief in one’s ability to plan and execute actions needed to manage different situations effectively.
Q26. Which of the following is an example of social self?
Answer – A) Identifying as a student of a school
Explanation: The social self refers to one’s identity in relation to social groups, roles, and affiliations like being a student, sibling, or citizen.
Q27. The difference between self-concept and self-esteem is:
Answer – B) Self-esteem is how much value you place on yourself
Explanation: Self-concept is the image or perception one has of oneself, while self-esteem reflects the value or worth one assigns to that self-image.
Q28. The ideal self represents:
Answer – C) The person you strive to become
Explanation: The ideal self is the version of oneself that one aspires to be — goals, dreams, and personal standards included.
Q29. The social self includes:
Answer – B) Their sense of social identity and group membership
Explanation: Social self refers to how one perceives themselves in relation to others — including roles, group identity, and social interactions.
Q30. Which of these is NOT a dimension of self?
Answer – B) Political self
Explanation: The main dimensions of the self are personal, social, and ideal. “Political self” is not a recognized psychological dimension of self in standard theories.
Q31. How is personality best described in psychology?
Answer – B) A combination of traits that make one unique
Explanation: Personality in psychology refers to the unique and consistent patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving that distinguish individuals from one another.
Q32. What does a well-developed sense of self contribute to?
Answer – B) Stronger identity and confidence
Explanation: A healthy self-concept leads to self-assurance, emotional well-being, and clarity about one’s values and goals, forming a strong personal identity.
Q33. What does behavioral analysis in personality assessment typically involve?
Answer – A) Observing behavior in natural settings
Explanation: Behavioral analysis assesses how individuals act in real-life or controlled situations, offering insights into their personality traits and responses.
Q34. The Rorschach Inkblot Test is categorized under which type of assessment?
Answer – C) Projective technique
Explanation: The Rorschach test uses ambiguous inkblots to uncover unconscious aspects of personality through spontaneous responses, making it a classic projective technique.
Q35. What type of material is used in the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)?
Answer – C) Ambiguous pictures
Explanation: The TAT presents vague images where individuals create stories, revealing underlying motives, conflicts, and personality aspects.
Q36. What is the primary focus of humanistic theories of personality?
Answer – B) Personal growth and self-actualization
Explanation: Humanistic theories, like those of Maslow and Rogers, emphasize the positive potential in people and focus on growth, free will, and reaching one’s full potential (self-actualization).
Q37. A child copying aggressive behavior seen in a parent is an example of:
Answer – C) Observational learning
Explanation: Observational learning, as explained by Bandura, happens when individuals watch and imitate others’ behaviors, especially those of role models like parents.
Q38. How did B.F. Skinner believe behavior is learned and maintained?
Answer – B) Reinforcement and punishment
Explanation: Skinner’s theory of operant conditioning suggests that behavior is influenced by the consequences it produces—rewards encourage repetition, while punishments reduce behavior.
Q39. What is the central idea behind the behavioral approach to personality?
Answer – C) Learning from environment
Explanation: Behavioral theories focus on observable behavior and emphasize that personality is shaped through learning and interactions with the environment.
Q40. According to Freud, what is the function of defense mechanisms?
Answer – B) Protect the ego from anxiety
Explanation: Freud proposed that defense mechanisms are unconscious processes that help reduce anxiety by distorting reality and protecting the ego from distressing thoughts or conflicts.
Q41. According to Freud, personality is structured into which of the following components?
Answer – C) Id, ego, and superego
Explanation: Freud suggested that personality has three main components: the id (instinctual drives), the ego (rational thinking), and the superego (moral conscience). These interact to influence behavior.
Q42. Which of the following is not one of the Big Five personality traits?
Answer – C) Humor
Explanation: The Big Five personality traits include Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism. Humor is not included as a core trait in this model.
Q43. How did Raymond Cattell assess personality?
Answer – B) 16 Personality Factor Questionnaire
Explanation: Cattell developed the 16PF, a standardized tool designed to measure basic personality traits using factor analysis.
Q44. In trait theory, traits are best defined as:
Answer – C) Relatively stable characteristics
Explanation: Traits are enduring patterns of behavior, thought, and emotion that tend to be consistent over time and across situations.
Q45. What classification of traits did Gordon Allport propose in his theory of personality?
Answer – B) Cardinal, central, and secondary traits
Explanation: Allport’s trait theory organized personality traits into three levels: cardinal (dominant traits), central (major traits of a person), and secondary (more situation-specific traits).
Q46. What is a major limitation of Type Approaches to personality?
Answer – B) They do not consider individual uniqueness
Explanation: Type Approaches categorize people into fixed types (like introvert or extrovert), often ignoring the complexity and uniqueness of each individual.
Q47. According to Sheldon’s body type theory, a mesomorph is described as:
Answer – C) Muscular and energetic
Explanation: Sheldon proposed that mesomorphs, who have a muscular and athletic build, tend to be bold, energetic, and action-oriented.
Q48. Who introduced the introvert–extrovert dimension of personality?
Answer – B) Jung
Explanation: Carl Jung was the first to define the concepts of introversion and extraversion as opposite personality orientations related to energy direction.
Q49. Studying personality allows psychologists to:
Answer – C) Predict consistent behavior patterns
Explanation: One key goal of personality psychology is to understand how individuals typically behave, think, and feel across different situations, aiding in prediction and support.
Q50. Which field of psychology is most directly connected to the study of self and personality?
Answer – D) Clinical psychology
Explanation: Clinical psychology deeply involves understanding individual personality and self-concept for diagnosing and treating psychological disorders.
Q51. Which of the following helps in enhancing self-efficacy?
Answer – A) Past success and encouragement
Explanation: Self-efficacy is strengthened by personal accomplishments, encouragement from others, and observing successful role models. These experiences build belief in one’s ability to succeed.
Q52. According to Bandura, self-efficacy refers to:
Answer – B) Confidence in your ability to perform specific tasks
Explanation: Bandura defined self-efficacy as an individual’s belief in their ability to organize and execute actions required to manage situations effectively.
Q53. In individualistic cultures, the self is usually viewed as:
Answer – C) Independent and unique
Explanation: Individualistic cultures, such as in the West, emphasize personal goals, uniqueness, and independence over group identity.
Q54. Which type of self is typically encouraged in Western cultures?
Answer – C) Independent self
Explanation: Western societies emphasize the independent self, where individuals prioritize autonomy, self-expression, and personal achievements.
Q55. Which psychologist is best known for developing the psychodynamic theory of personality?
Answer – C) Sigmund Freud
Explanation: Freud is the pioneer of the psychodynamic approach, which explores unconscious motives, childhood experiences, and inner conflicts in shaping personality.
Q56. Who proposed a personality theory linking behavior with bodily fluids or humors?
Answer – C) Hippocrates
Explanation: Hippocrates suggested that human temperament was shaped by an imbalance in four bodily fluids—blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile—marking one of the earliest biological perspectives on personality.
Q57. What defines a self-report personality test?
Answer – C) Filled out by individuals about their own traits and behavior
Explanation: A self-report inventory collects responses directly from individuals, who evaluate and report on their own personality characteristics.
Q58. Which of the following is an example of a self-report inventory used to assess personality?
Answer – C) 16 Personality Factor Questionnaire
Explanation: Cattell’s 16PF is a structured questionnaire in which individuals respond to items revealing consistent behavioral patterns across 16 key traits.
Q59. On what idea are projective tests based?
Answer – B) People reveal their hidden emotions through ambiguous prompts
Explanation: Projective techniques like the TAT or Rorschach operate on the belief that when faced with vague or unstructured stimuli, individuals unconsciously project their personal conflicts, desires, and fears onto the situation.
Q60. What would a psychologist explore under the topic of ‘Self and Personality’?
Answer – C) Thoughts, emotions, and personal identity
Explanation: The study of self and personality examines how individuals view themselves, how they emotionally respond, and how personality patterns influence behavior across different contexts.
Q61. Which of the following best describes the Draw-A-Person Test used in personality assessment?
Answer – C) Projective technique
Explanation: The Draw-A-Person Test allows individuals to express unconscious feelings through drawings, making it a projective technique often used in clinical settings.
Q62. Which of the following is considered a projective method of personality testing?
Answer – B) Rorschach Inkblot Test
Explanation: The Rorschach test uses ambiguous inkblots to reveal hidden emotions and conflicts, making it a classic projective tool.
Q63. What does self-regulation primarily involve?
Answer – B) Controlling thoughts, emotions, and behaviors
Explanation: Self-regulation means managing your emotions, thoughts, and actions to reach personal goals and handle challenges effectively.
Q64. A student who ignores distractions to complete homework shows which of the following?
Answer – B) Strong self-regulation
Explanation: Staying focused and resisting temptation to complete a task is a classic example of effective self-regulation.
Q65. What does the Type Approach to personality aim to do?
Answer – C) Group people by bodily or personality traits
Explanation: Type approaches divide individuals into fixed categories based on observable patterns, such as body shape (Sheldon) or temperament (Hippocrates).
Q66. On what basis did Hippocrates classify different personality types?
Answer – B) Bodily fluids (humors)
Explanation: Hippocrates proposed that personality traits stemmed from the balance of four body fluids — blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile — a theory known as the humor-based classification.
Q67. Which of the following is commonly used in behavioral assessment of personality?
Answer – B) Role-play
Explanation: Role-play allows psychologists to observe how individuals respond to specific situations, making it a practical tool in behavioral assessments.
Q68. How is personality generally understood in Indian philosophical thought?
Answer – C) An interplay of spiritual, mental, and physical aspects
Explanation: Indian tradition views personality as a holistic combination of body, mind, and soul, emphasizing balance and self-realization.
Q69. What is the central idea behind humanistic theories of personality?
Answer – B) Personal growth and self-actualization
Explanation: Humanistic theories focus on the individual’s natural drive to achieve personal growth, reach full potential, and pursue self-fulfillment.
Q70. What does Maslow describe as the highest level in his hierarchy of needs?
Answer – D) Self-actualization
Explanation: Maslow’s theory places self-actualization — the realization of one’s full potential and creativity — at the top of the hierarchy of needs.
Self and Personality (Important Overview)
1. Important People (Name + Contribution)
- Sigmund Freud – Developed the Psychoanalytic theory of personality (Id, Ego, Superego)
- Carl Jung – Introduced concepts like Personal Unconscious and Collective Unconscious
- Alfred Adler – Gave the idea of Individual Psychology and striving for superiority
- Karen Horney – Focused on social and cultural factors affecting personality, criticized Freud’s views on women
- Erik Erikson – Proposed the Psychosocial stages of development across life
- Carl Rogers – Developed Humanistic theory, emphasizing Self-concept and Unconditional Positive Regard
- Abraham Maslow – Proposed the Hierarchy of Needs and the idea of self-actualization
- Albert Bandura – Introduced the concept of Observational Learning and Self-efficacy in personality
- Gordon Allport – Studied Traits; proposed cardinal, central, and secondary traits
- Raymond Cattell – Used factor analysis to identify 16 personality factors
- Hans Eysenck – Proposed a 3-dimensional model: Extraversion-Introversion, Neuroticism-Stability, Psychoticism
- Robert McCrae & Paul Costa – Developed the Five-Factor Model (Big Five Personality Traits)
2. Important Theories / Laws / Models of Self and Personality
- Freud’s Psychoanalytic Theory – Personality is shaped by unconscious motives; structure: Id, Ego, Superego
- Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory – Personality develops through 8 stages across lifespan
- Humanistic Theories – Emphasize personal growth, self-actualization (Maslow, Rogers)
- Trait Theories – Focus on measuring traits that make up personality (Allport, Cattell, Eysenck, Big Five)
- Behavioral & Social Learning Theories – Emphasize learning from environment and modeling (Bandura)
- Self Concept – How a person views themselves, including Self-esteem and Self-efficacy
- Projective Techniques – Tools to assess unconscious personality aspects (e.g., Rorschach Inkblot Test, TAT)
3. Important Terms to Highlight
- Self – Organized, consistent set of beliefs and perceptions about oneself
- Self-concept – Overall view a person has about themselves
- Self-esteem – Value or worth a person attaches to themselves
- Self-efficacy – Belief in one’s ability to succeed
- Personality – Unique and relatively stable patterns of behavior, thoughts, and emotions
- Trait – A stable characteristic influencing behavior
- Unconscious – Reservoir of thoughts, memories, and desires outside conscious awareness
- Id, Ego, Superego – Structural components of mind according to Freud
- Defense Mechanisms – Strategies used unconsciously to protect oneself from anxiety (e.g., repression, denial)
- Self-actualization – Realizing one’s fullest potential (Maslow)
- Five-Factor Model – Broad dimensions: Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, Neuroticism (OCEAN)
- Social Cognitive Approach – Emphasizes personal experiences, interpretation, and observational learning
4. Important Tables
Table: Freud’s Structure of Personality
| Component | Description | Principle | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Id | Instinctual drives | Pleasure principle | Wanting immediate gratification |
| Ego | Rational part | Reality principle | Delaying gratification |
| Superego | Moral conscience | Moral principle | Feeling guilty for bad behavior |
Table: Erikson’s Eight Stages of Psychosocial Development
| Stage | Age Range | Conflict | Key Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Trust vs. Mistrust | 0–1.5 years | Can I trust the world? | |
| 2. Autonomy vs. Shame | 1.5–3 years | Can I do things myself? | |
| 3. Initiative vs. Guilt | 3–5 years | Is it okay for me to do things? | |
| 4. Industry vs. Inferiority | 6–12 years | Can I succeed in the world? | |
| 5. Identity vs. Role Confusion | 12–18 years | Who am I? | |
| 6. Intimacy vs. Isolation | Young adulthood | Can I love and be loved? | |
| 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation | Middle adulthood | Can I make my life count? | |
| 8. Integrity vs. Despair | Late adulthood | Was my life meaningful? |
Table: Five-Factor Model (Big Five Traits)
| Trait | Description |
|---|---|
| Openness | Imagination, creativity, openness to new experiences |
| Conscientiousness | Organized, responsible, dependable |
| Extraversion | Sociable, energetic, assertive |
| Agreeableness | Cooperative, warm, caring |
| Neuroticism | Emotional instability, anxiety, moodiness |

