Table of Contents
Unit 1: Variations in Psychological Attributes PYQs & MCQs
Q1. Which option correctly describes psychological attributes?
Answer – B) Characteristics like intelligence, personality, and aptitude
Explanation: Psychological attributes refer to internal qualities such as intelligence, creativity, personality, and values. These are not directly observable but can be assessed through psychological tools.
Q2. Why is it important to study individual differences in psychological attributes?
Answer – C) It promotes personalized development and learning
Explanation: Understanding individual differences allows educators and professionals to design interventions, teaching strategies, and developmental plans tailored to each person’s unique strengths and needs.
Q3. What is one key feature of a well-constructed psychological test?
Answer – B) Validity
Explanation: Validity refers to how accurately a test measures what it is intended to measure. Without validity, a test cannot provide meaningful or reliable results.
Q4. In psychological testing, what does the term “validity” mean?
Answer – B) Extent to which test measures what it claims to measure
Explanation: Validity is crucial in ensuring that the conclusions drawn from a test are accurate. If a test claims to measure intelligence, it should not measure memory or personality instead.
Q5. How does intelligence assist individuals in daily life?
Answer – C) Adjust effectively to their surroundings
Explanation: Intelligence helps people analyze situations, make sound decisions, and solve problems, thereby adapting successfully to their environment.
Q6. Who described intelligence as the overall ability to act with purpose, think rationally, and effectively adapt to the environment?
Answer – C) Wechsler
Explanation: David Wechsler defined intelligence as the global capacity of an individual to act purposefully, think rationally, and deal effectively with their environment — a widely accepted definition in psychology.
Q7. What are the two components of intelligence according to Spearman’s theory?
Answer – B) G (general) and S (specific) factors
Explanation: Spearman’s two-factor theory suggested that intelligence has a general factor (G) that influences performance across all tasks and specific factors (S) that apply to particular tasks.
Q8. Which of the following is not a part of Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences?
Answer – D) Mechanical
Explanation: Gardner proposed intelligences like linguistic, musical, spatial, and logical-mathematical, among others. “Mechanical” is not one of the intelligences in his model.
Q9. Who introduced the concept of “mental age” in the study of intelligence?
Answer – B) Binet and Simon
Explanation: Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon introduced the concept of mental age to identify children needing special help in school. This laid the foundation for later intelligence testing.
Q10. As per the American Psychological Association (APA), which of the following is not considered a component of intelligence?
Answer – C) Physical coordination
Explanation: Intelligence involves abilities like abstract reasoning, learning, adaptation, and problem-solving. Physical coordination relates more to motor skills than to cognitive intelligence.
Q11. Which of the following best defines intelligence?
Answer – B) Capacity to learn, reason, and solve problems
Explanation: Intelligence refers to the mental ability to acquire knowledge, apply logic, adapt to new situations, and solve complex problems — not just rote learning.
Q12. Which of the following is not considered a psychological assessment tool?
Answer – C) Thermometer
Explanation: A thermometer measures body temperature, not psychological traits. Psychological assessment tools are designed to evaluate mental and emotional characteristics.
Q13. What does it mean if a psychological test is reliable?
Answer – C) Gives consistent results over time
Explanation: Reliability refers to the consistency of a test. A reliable psychological test yields similar results when administered under similar conditions at different times.
Q14. Which of the following is an example of an intra-individual difference?
Answer – A) Ramesh is better in science than in languages
Explanation: Intra-individual differences refer to variations within the same person. Ramesh performing differently in two subjects is a clear case of this.
Q15. Which of the following does not play a role in causing individual differences?
Answer – D) Identical life experiences
Explanation: If individuals go through identical life experiences, they are less likely to show major differences. In reality, differences arise due to diverse environments, heredity, and personal factors.
Q16. Why is it useful to understand variations in psychological attributes among individuals?
Answer – C) Guiding individuals to choose suitable careers
Explanation: Understanding psychological differences helps in identifying each person’s strengths and potential, which is essential for career guidance, educational planning, and personal development.
Q17. What does the psychological attribute “aptitude” help in identifying?
Answer – C) Potential for success in specific areas
Explanation: Aptitude refers to the innate or acquired capacity to perform well in particular domains like music, math, or engineering. It helps predict future performance in specific areas.
Q18. What is the full form of the abbreviation “IQ” in psychology?
Answer – D) Intelligence Quotient
Explanation: IQ stands for Intelligence Quotient. It is a score derived from standardized tests designed to measure a person’s intellectual ability relative to others.
Q19. According to Sternberg’s triarchic theory, which of the following is not a part of intelligence?
Answer – D) Musical intelligence
Explanation: Sternberg’s triarchic theory includes analytical, creative, and practical intelligence. Musical intelligence is part of Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences, not Sternberg’s.
Q20. Who is credited with introducing the concept of emotional intelligence?
Answer – A) Goleman
Explanation: Daniel Goleman popularized the concept of emotional intelligence, which involves recognizing, understanding, and managing emotions in oneself and others.
Q21. How is the relationship between culture and intelligence best understood?
Answer – C) Culture shapes how intelligence is defined and expressed
Explanation: Cultural contexts influence what is considered intelligent behavior, as well as how intelligence is assessed and manifested in individuals.
Q22. Which of the following would be considered a culturally biased or loaded test item?
Answer – B) A question about local traditions
Explanation: Test items that rely on culturally specific knowledge, like local customs or traditions, are considered culturally loaded and may disadvantage those unfamiliar with that culture.
Q23. Emotional intelligence plays a crucial role in which area?
Answer – C) Leadership and teamwork
Explanation: Emotional intelligence is vital for recognizing and managing emotions in oneself and others, which enhances communication, cooperation, leadership, and group dynamics.
Q24. Which of the following statements about emotional intelligence is correct?
Answer – C) Emotional intelligence can be developed through training and awareness
Explanation: Emotional intelligence is a skill that can be nurtured and improved through self-reflection, practice, and emotional training programs.
Q25. What do “special abilities” in psychology typically refer to?
Answer – C) Exceptional talents or capabilities in specific areas
Explanation: Special abilities refer to heightened talents in particular domains such as music, mathematics, or athletics, often observed in gifted individuals.
Q26. A person who shows outstanding talent in areas such as painting or music is said to possess:
Answer – B) A special ability
Explanation: Exceptional performance in areas like art or music reflects a special ability — a specific talent that stands out from general capabilities and is often nurtured through practice and exposure.
Q27. Which of the following best defines the concept of aptitude?
Answer – B) Inborn potential for learning a skill
Explanation: Aptitude is an innate ability that indicates a person’s potential to learn and succeed in a particular area with training and experience.
Q28. Which of the following is not considered a type of special ability?
Answer – D) Shyness
Explanation: Shyness is a personality trait, not a cognitive or intellectual skill. Special abilities involve enhanced capabilities in specific domains like numbers, space, or language.
Q29. If a young child demonstrates extraordinary talent in mathematics, they are most likely to have:
Answer – C) A special ability
Explanation: A child prodigy in mathematics is considered to have a special ability or giftedness in that particular domain, which exceeds average developmental expectations.
Q30. How is creativity best understood in psychological terms?
Answer – B) Producing novel and useful ideas
Explanation: Creativity involves generating original ideas or approaches that are both innovative and functional. It reflects flexibility in thought and problem-solving.

Q31. An individual who generates multiple ideas and approaches for solving a problem is engaging in:
Answer – B) Divergent thinking
Explanation: Divergent thinking involves producing many different solutions or ideas for a single problem. It reflects creativity and is key in brainstorming and innovation.
Q32. Who defined creativity as the ability to produce work that is both novel and appropriate?
Answer – C) Robert Sternberg
Explanation: Robert Sternberg described creativity as the capacity to create ideas or products that are both original and suitable to the context — highlighting usefulness alongside novelty.
Q33. Which of the following tools is primarily used to assess aptitude?
Answer – C) Differential Aptitude Test (DAT)
Explanation: The DAT is specifically designed to evaluate a person’s potential to succeed in specific areas, making it ideal for measuring aptitude across domains like reasoning, numerical ability, and mechanical understanding.
Q34. A student who excels in abstract reasoning is most likely to perform well in which kind of test?
Answer – C) Aptitude test
Explanation: Abstract reasoning is often a core component of aptitude tests as it reflects problem-solving ability and logical thinking — skills important in academic and professional settings.
Q35. What are key characteristics of a well-constructed aptitude test?
Answer – C) Standardized and reliable
Explanation: A good aptitude test is both standardized (uniform in administration and scoring) and reliable (produces consistent results), ensuring fairness and accuracy in assessing potential.
Q36. What does empathy as a component of emotional intelligence involve?
Answer – C) Understanding and sharing the feelings of others
Explanation: Empathy means being able to recognize, understand, and respond appropriately to the emotions of others, which helps in building meaningful relationships.
Q37. Emotional intelligence plays a vital role in:
Answer – B) Better interpersonal relationships
Explanation: Emotional intelligence helps individuals understand and manage emotions, which improves communication, empathy, and cooperation — all essential for healthy social and professional relationships.
Q38. One of the key criticisms of traditional intelligence tests is that:
Answer – C) It often reflects the culture of the test-maker
Explanation: Traditional IQ tests are often criticized for cultural bias — the language, examples, and content may favor individuals from certain backgrounds, making it unfair for others.
Q39. While intelligence is considered a universal trait, its expression is:
Answer – C) Shaped by cultural norms and values
Explanation: Though intelligence is present in all humans, its development and how it’s expressed varies across societies due to differences in cultural values, learning systems, and environmental influences.
Q40. If a child’s mental age is 10 years and chronological age is 8 years, what will their IQ be?
Answer – B) 125
Explanation: IQ is calculated using the formula: (Mental Age / Chronological Age) × 100. So, (10 / 8) × 100 = 125.
Q41. What influences an individual’s intelligence most accurately?
Answer – C) Both heredity and environment
Explanation: Intelligence develops through the combined effects of genetic inheritance and environmental influences such as education, culture, and life experiences.
Q42. In which of the following situations is observation as a method of assessment most appropriate?
Answer – B) Assessing behavior in natural settings
Explanation: Observation is commonly used in psychology to understand how individuals behave in their natural environments without interference.
Q43. Who stressed the uniqueness of individuals by stating that no two people are exactly alike?
Answer – B) Galton
Explanation: Sir Francis Galton, a pioneer in the study of individual differences, emphasized that every person is unique in their traits and abilities.
Q44. What is most useful in understanding differences in how people think, feel, and behave?
Answer – B) Study of psychological attributes
Explanation: Psychological attributes such as intelligence, personality, and motivation help explain why individuals differ in their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
Q45. Which of the following is not included under the term “psychological attributes”?
Answer – D) Height
Explanation: Height is a physical trait, not a psychological attribute. Psychological attributes refer to mental characteristics like intelligence, attitude, personality, and motivation.
Q46. What do individual differences primarily refer to in psychology?
Answer – B) Variations in behavior, thinking, and emotions among people
Explanation: Individual differences focus on how people differ in mental traits such as intelligence, emotions, personality, and behavior patterns — making each person psychologically unique.
Q47. What is the primary focus of the psychological assessment process?
Answer – B) Collecting information using standardized tools
Explanation: Psychological assessment involves gathering structured data using validated tools like tests, interviews, and observation methods to evaluate mental functions and behavior.
Q48. According to Gardner’s theory, someone skilled in understanding others’ emotions and intentions shows high:
Answer – C) Interpersonal intelligence
Explanation: Interpersonal intelligence refers to the ability to understand and interact effectively with others, including sensitivity to moods, motivations, and emotions.
Q49. What is the main goal of a culture-fair intelligence test?
Answer – C) Minimize cultural influences on test performance
Explanation: Culture-fair tests are designed to reduce the impact of language, background, and culture so that individuals from different environments can be assessed fairly.
Q50. In rural traditional communities, how is intelligence most likely to be viewed?
Answer – C) Practical problem-solving in natural settings
Explanation: In rural and traditional societies, intelligence is often recognized through practical abilities — like adapting to environmental challenges or solving everyday problems effectively.
VERY USEFUL FOR CUET UG PSYCHOLOGY EXAM
Important People (Name + Contribution)
- Alfred Binet – Created the first practical intelligence test to assess children’s mental abilities, focusing on identifying learning difficulties.
- Lewis Terman – Revised Binet’s test for American use, leading to the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale; introduced the concept of Intelligence Quotient (IQ).
- David Wechsler – Developed intelligence tests for different age groups (WAIS for adults, WISC for children), emphasizing both verbal and performance abilities.
- Charles Spearman – Proposed the Two-Factor Theory of Intelligence, introducing the ideas of general intelligence (g-factor) and specific abilities (s-factors).
- Louis Thurstone – Suggested that intelligence consists of several Primary Mental Abilities instead of a single factor, such as verbal comprehension and numerical ability.
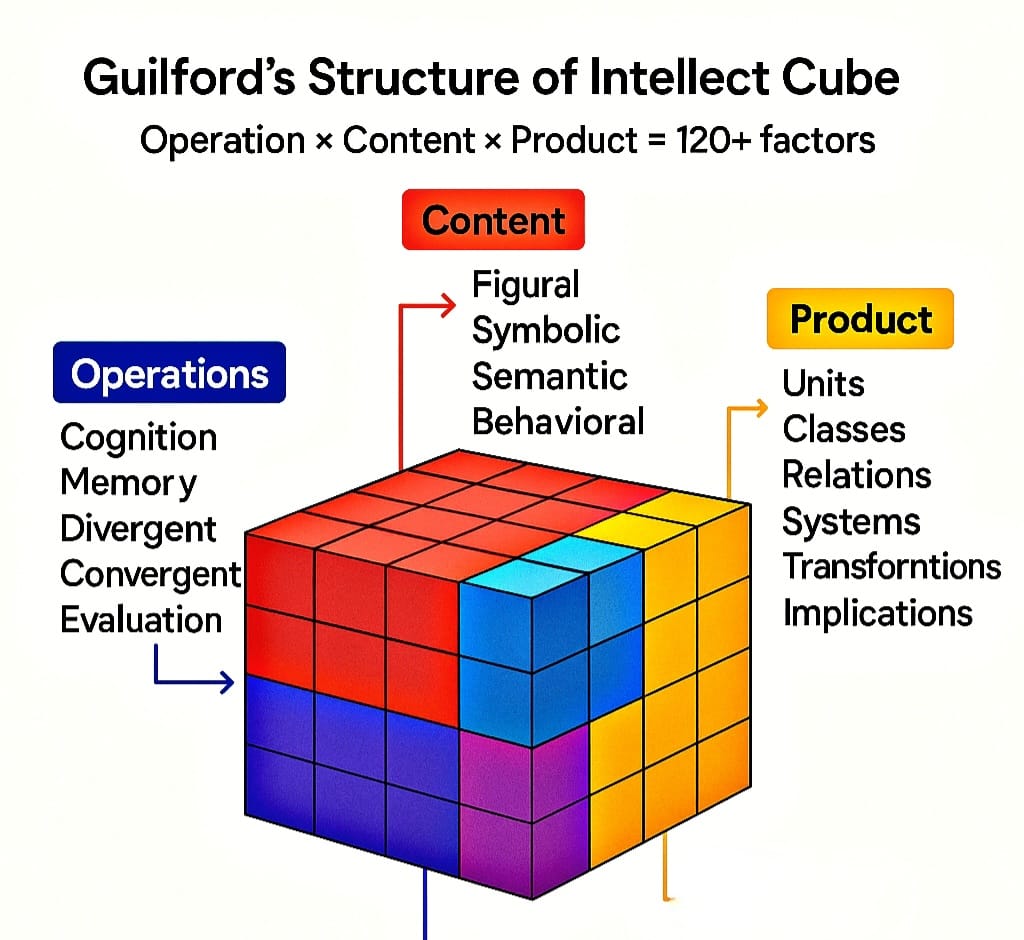
- J.P. Guilford – Designed the Structure of Intellect Model, explaining intelligence through three dimensions: operations, contents, and products, leading to a wide variety of mental abilities.
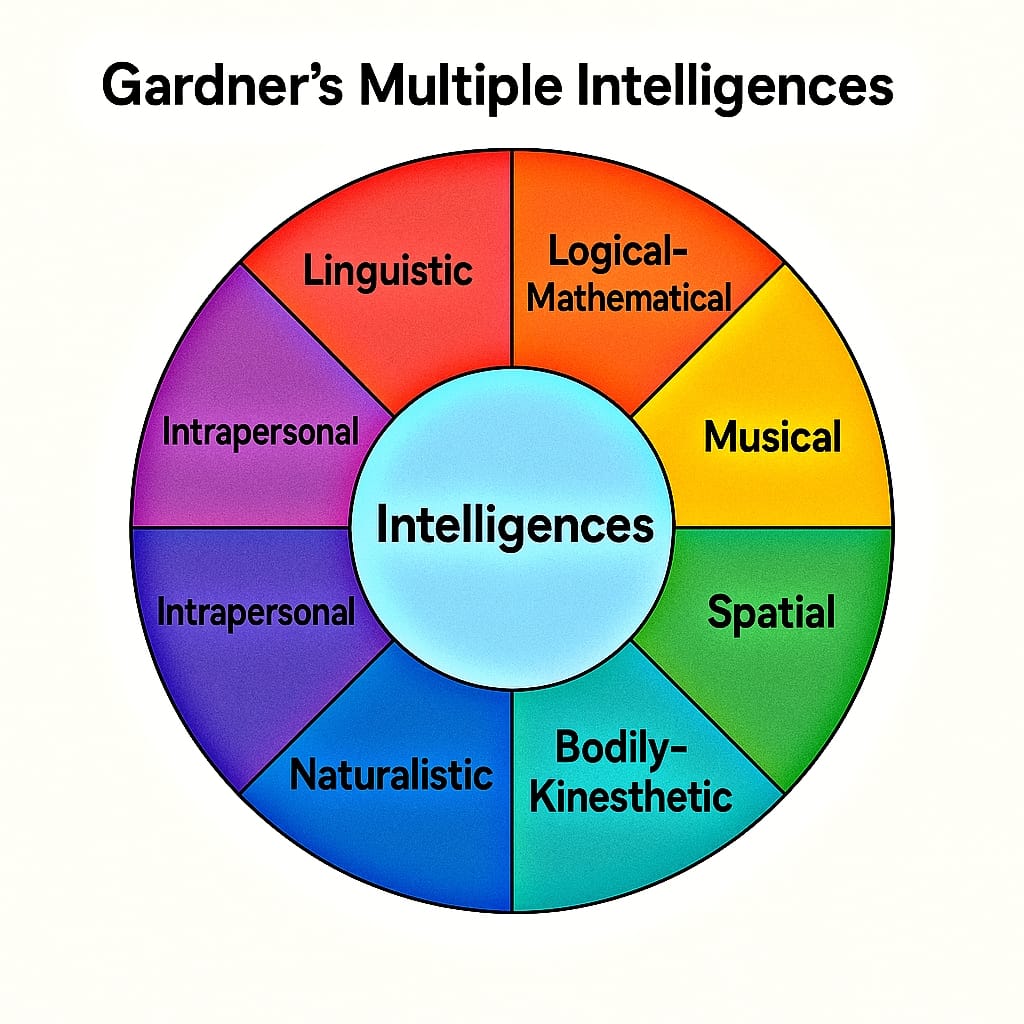
- Howard Gardner – Proposed the Theory of Multiple Intelligences, suggesting that intelligence is not a single ability but a collection of different types like linguistic, musical, bodily-kinesthetic, and more.
- Robert Sternberg – Introduced the Triarchic Theory of Intelligence, describing intelligence in three parts: analytical skills, creative abilities, and practical problem-solving.
- Salovey and Mayer – Coined the concept of Emotional Intelligence, focusing on the ability to perceive, manage, and regulate emotions effectively.
- Daniel Goleman – Popularized the concept of Emotional Intelligence for a wider audience, highlighting its importance in personal and professional success.
Important Theories / Laws / Models
- Spearman’s Two-Factor Theory – Intelligence has two components: a general ability (g) common to all tasks, and specific abilities (s) unique to particular tasks.
- Thurstone’s Primary Mental Abilities – Intelligence consists of several independent factors, such as verbal ability, reasoning, and perceptual speed.
- Guilford’s Structure of Intellect Model – Intelligence is explained through a three-dimensional model (operations, contents, products) producing many combinations of mental abilities.
- Gardner’s Theory of Multiple Intelligences – Intelligence is not a single ability but a collection of multiple independent intelligences like linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, musical, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalistic.
- Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory of Intelligence – Intelligence involves three interrelated aspects: analytical intelligence (problem-solving), creative intelligence (novel ideas), and practical intelligence (everyday tasks).
- Emotional Intelligence Concept – Focuses on recognizing, understanding, managing, and using emotions in positive ways to communicate effectively and overcome challenges.
Important Terms to Highlight: Variations in Psychological Attributes
- Intelligence – The global ability to understand the world, think logically, and use resources effectively when faced with challenges.
- Aptitude – A natural or acquired ability to perform specific tasks, often seen as potential for future learning or success in a particular area.
- Creativity – The ability to produce ideas, solutions, or products that are both novel (original) and appropriate (useful).
- Emotional Intelligence – The skill to perceive, express, understand, and manage emotions in oneself and others.
- IQ (Intelligence Quotient) – A numerical expression of intelligence calculated by comparing mental age (MA) to chronological age (CA).
- Mental Age (MA) – The level of intellectual functioning typically associated with a certain chronological age.
- Chronological Age (CA) – A person’s actual age measured in years from birth.
- IQ Formula –
IQ = (Mental Age ÷ Chronological Age) × 100 - Normal Probability Curve – A bell-shaped curve showing the distribution of intelligence scores in a population, where most scores cluster around the average.
- Culture Fair Tests – Intelligence tests designed to minimize the influence of cultural background, language, and education.
- Individual vs Group Testing –
- Individual Testing: One-on-one testing situation, allows for detailed observation.
- Group Testing: Conducted with many individuals at once, quicker and more economical.
- Verbal vs Non-Verbal Tests –
- Verbal Tests: Require language-based responses.
- Non-Verbal Tests: Use symbols, pictures, or puzzles to assess intelligence.
- Assessment vs Evaluation –
- Assessment: Process of gathering information for understanding and improvement.
- Evaluation: Judging the value or quality based on set criteria.
Tables to remember
Table 1: Major Theories of Intelligence
| Theory/Model | Proposed By | Key Idea |
|---|---|---|
| Two-Factor Theory | Charles Spearman | Intelligence has a general factor (g) and specific factors (s). |
| Primary Mental Abilities | Louis Thurstone | Intelligence is a set of independent abilities like verbal, numerical. |
| Structure of Intellect Model | J.P. Guilford | Intelligence has 3 dimensions (operations, contents, products). |
| Multiple Intelligences | Howard Gardner | Intelligence is multiple independent abilities (linguistic, musical, etc.). |
| Triarchic Theory | Robert Sternberg | Intelligence includes analytical, creative, and practical skills. |
Table 2: Differences between Intelligence, Aptitude, and Creativity
| Concept | Definition | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligence | Overall mental ability to understand, reason, and solve problems. | General mental capacity |
| Aptitude | Specific ability or potential to learn skills. | Future learning potential |
| Creativity | Ability to produce novel and useful ideas or products. | Original thinking and innovation |
Table 3: Verbal vs Non-Verbal Tests
| Feature | Verbal Tests | Non-Verbal Tests |
|---|---|---|
| Based On | Language (words, sentences) | Symbols, diagrams, patterns |
| Requires Literacy | Yes | No |
| Example | Vocabulary test | Raven’s Progressive Matrices |
| Usage | Academic assessments | Cross-cultural testing |
Table 4: Individual vs Group Intelligence Testing
| Feature | Individual Testing | Group Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Administration | One-to-one | Many people together |
| Time Required | More time-consuming | Time-saving |
| Observation | Detailed observation possible | Limited observation |
| Example | Stanford-Binet Test | Army Alpha and Beta Tests |
Table 5: Mental Age, Chronological Age, and IQ Relationship
| Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Mental Age (MA) | Age level at which a person functions mentally | A 10-year-old solving 12-year tasks has MA = 12 |
| Chronological Age (CA) | Actual age from birth | 10 years |
| IQ Formula | (Mental Age ÷ Chronological Age) × 100 | (12 ÷ 10) × 100 = 120 |
Table 6: Types of Aptitude Tests
| Type of Aptitude Test | Focus Area | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Aptitude | Understanding of mechanical concepts | Engineering entrance exams |
| Clerical Aptitude | Speed and accuracy in clerical work | Bank clerical exams |
| Numerical Aptitude | Handling numbers and calculations | Accounting tests |
| Artistic Aptitude | Creative expression in art or design | Designing and architecture tests |
Table 7: Characteristics of a Normal Probability Curve (for Intelligence Distribution)
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Shape | Bell-shaped and symmetrical |
| Mean, Median, Mode | All are equal and located at the center |
| Distribution of Scores | Most scores cluster around the mean; few are extreme |
| Percentage Distribution | 68% within 1 SD, 95% within 2 SD, 99.7% within 3 SD |
Table 8: Assessment vs Evaluation
| Feature | Assessment | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To collect information for improvement | To judge the value or quality |
| Nature | Descriptive, ongoing | Judgmental, conclusive |
| Example | Giving feedback after a practice test | Grading in final exams |
Table 9: Culture Fair Tests vs Culture Biased Tests
| Feature | Culture Fair Tests | Culture Biased Tests |
|---|---|---|
| Dependence on Culture | Minimized | High |
| Language Dependency | Low | High |
| Example | Raven’s Progressive Matrices | Verbal analogies test |
| Purpose | True measure of intelligence | May reflect educational background |

